A noncatalytic function of the ligation complex during nonhomologous end joining
- PMID: 23337116
- PMCID: PMC3549972
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201203128
A noncatalytic function of the ligation complex during nonhomologous end joining
Abstract
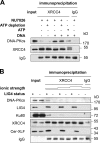
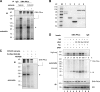
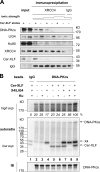
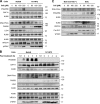
Nonhomologous end joining is the primary deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) double-strand break repair pathway in multicellular eukaryotes. To initiate repair, Ku binds DNA ends and recruits the DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) forming the holoenzyme. Early end synapsis is associated with kinase autophosphorylation. The XRCC4 (X4)-DNA Ligase IV (LIG4) complex (X4LIG4) executes the final ligation promoted by Cernunnos (Cer)-X4-like factor (XLF). In this paper, using a cell-free system that recapitulates end synapsis and DNA-PKcs autophosphorylation, we found a defect in both activities in human cell extracts lacking LIG4. LIG4 also stimulated the DNA-PKcs autophosphorylation in a reconstitution assay with purified components. We additionally uncovered a kinase autophosphorylation defect in LIG4-defective cells that was corrected by ectopic expression of catalytically dead LIG4. Finally, our data support a contribution of Cer-XLF to this unexpected early role of the ligation complex in end joining. We propose that productive end joining occurs by early formation of a supramolecular entity containing both DNA-PK and X4LIG4-Cer-XLF complexes on DNA ends.
Figures


Similar articles
-
DNA-dependent protein kinase regulates DNA end resection in concert with Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 (MRN) and ataxia telangiectasia-mutated (ATM).J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 27;288(52):37112-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.514398. Epub 2013 Nov 12. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24220101 Free PMC article.
-
An Intrinsically Disordered APLF Links Ku, DNA-PKcs, and XRCC4-DNA Ligase IV in an Extended Flexible Non-homologous End Joining Complex.J Biol Chem. 2016 Dec 30;291(53):26987-27006. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.751867. Epub 2016 Nov 14. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27875301 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between Cernunnos-XLF and nonhomologous end-joining proteins at DNA ends in the cell.J Biol Chem. 2007 Nov 2;282(44):31937-43. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704554200. Epub 2007 Aug 24. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17720816
-
Detection and repair of ionizing radiation-induced DNA double strand breaks: new developments in nonhomologous end joining.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013 Jul 1;86(3):440-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.01.011. Epub 2013 Feb 20. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013. PMID: 23433795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
XRCC4 and XLF form long helical protein filaments suitable for DNA end protection and alignment to facilitate DNA double strand break repair.Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Feb;91(1):31-41. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2012-0058. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23442139 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unravelling the complexities of DNA-PK activation by structure-based mutagenesis.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 13:rs.3.rs-3627471. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3627471/v1. Res Sq. 2023. PMID: 38168382 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
A single XLF dimer bridges DNA ends during nonhomologous end joining.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2018 Sep;25(9):877-884. doi: 10.1038/s41594-018-0120-y. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30177755 Free PMC article.
-
TIRR: a potential front runner in HDR race-hypotheses and perspectives.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Mar;47(3):2371-2379. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05285-x. Epub 2020 Feb 8. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32036573 Review.
-
DNA Ligase IV Guides End-Processing Choice during Nonhomologous End Joining.Cell Rep. 2017 Sep 19;20(12):2810-2819. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.08.091. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28930678 Free PMC article.
-
ATM antagonizes NHEJ proteins assembly and DNA-ends synapsis at single-ended DNA double strand breaks.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Sep 25;48(17):9710-9723. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa723. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32890395 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akopiants K., Zhou R.Z., Mohapatra S., Valerie K., Lees-Miller S.P., Lee K.J., Chen D.J., Revy P., de Villartay J.P., Povirk L.F. 2009. Requirement for XLF/Cernunnos in alignment-based gap filling by DNA polymerases lambda and mu for nonhomologous end joining in human whole-cell extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:4055–4062 10.1093/nar/gkp283 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

