Helios marks strongly autoreactive CD4+ T cells in two major waves of thymic deletion distinguished by induction of PD-1 or NF-κB
- PMID: 23337809
- PMCID: PMC3570102
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20121458
Helios marks strongly autoreactive CD4+ T cells in two major waves of thymic deletion distinguished by induction of PD-1 or NF-κB
Abstract
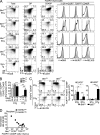
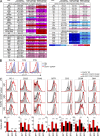
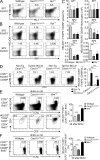
Acquisition of self-tolerance in the thymus requires T cells to discriminate strong versus weak T cell receptor binding by self-peptide-MHC complexes. We find this discrimination is reported by expression of the transcription factor Helios, which is induced during negative selection but decreases during positive selection. Helios and the proapoptotic protein Bim were coinduced in 55% of nascent CCR7(-) CD4(+) CD69(+) thymocytes. These were short-lived cells that up-regulated PD-1 and down-regulated CD4 and CD8 during Bim-dependent apoptosis. Helios and Bim were also coinduced at the subsequent CCR7(+) CD4(+) CD69(+) CD8(-) stage, and this second wave of Bim-dependent negative selection involved 20% of nascent cells. Unlike CCR7(-) counterparts, Helios(+) CCR7(+) CD4(+) cells mount a concurrent Card11- and c-Rel-dependent activation response that opposes Bim-mediated apoptosis. This "hollow" activation response consists of many NF-κB target genes but lacks key growth mediators like IL-2 and Myc, and the thymocytes were not induced to proliferate. These findings identify Helios as the first marker known to diverge during positive and negative selection of thymocytes and reveal the extent, stage, and molecular nature of two distinct waves of clonal deletion in the normal thymus.
Figures





References
-
- Baldwin T.A., Hogquist K.A. 2007. Transcriptional analysis of clonal deletion in vivo. J. Immunol. 179:837–844 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

