Bullous pemphigoid IgG induces BP180 internalization via a macropinocytic pathway
- PMID: 23337823
- PMCID: PMC3590760
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.11.029
Bullous pemphigoid IgG induces BP180 internalization via a macropinocytic pathway
Abstract
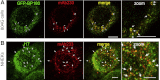
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is an autoimmune blistering skin disease induced by pathogenic autoantibodies against a type II transmembrane protein (BP180, collagen type XVII, or BPAG2). In animal models, BP180 autoantibody-antigen interaction appears insufficient to develop blisters, but involvement of complement and neutrophils is required. However, cultured keratinocytes treated with BP-IgG exhibit a reduction in the adhesive strength and a loss of expression of BP180, suggesting that the autoantibodies directly affect epidermal cell-extracellular matrix integrity. In this study, we explored the consequences of two distinct epithelial cells treated with BP-IgG, particularly the fate of BP180. First, we followed the distribution of green fluorescent protein-tagged BP180 in an epithelial cell line, 804G, and normal human epidermal keratinocytes after autoantibody clustering. After BP-IgG treatment, the adhesive strength of the cells to their substrate was decreased, and BP180 was internalized in both cell types, together with the early endosomal antigen-1. By using various endocytosis inhibitors and a fluid-uptake assay, we demonstrated that BP-IgG-induced BP180 internalization is mediated via a macropinocytic pathway. Moreover, a macropinocytosis inhibitor rescued a BP-IgG-induced reduction in the adhesive strength of the cells from their substrate. The results of this study suggest that BP180 internalization induced by BP-IgG plays an important role in the initiation of disease pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2013 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
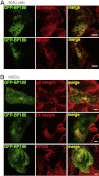

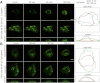

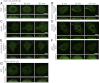


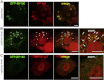
References
-
- Lever W.F. Pemphigus. Medicine (Baltimore) 1953;32:1–123. - PubMed
-
- Jordon R.E., Beutner E.H., Witebsky E., Blumental G., Hale W.L., Lever W.F. Basement zone antibodies in bullous pemphigoid. JAMA. 1967;200:751–756. - PubMed
-
- Labib R.S., Anhalt G.J., Patel H.P., Mutasim D.F., Diaz L.A. Molecular heterogeneity of the bullous pemphigoid antigens as detected by immunoblotting. J Immunol. 1986;136:1231–1235. - PubMed
-
- Diaz L.A., Ratrie H., 3rd, Saunders W.S., Futamura S., Squiquera H.L., Anhalt G.J., Giudice G.J. Isolation of a human epidermal cDNA corresponding to the 180-kD autoantigen recognized by bullous pemphigoid and herpes gestationis sera: immunolocalization of this protein to the hemidesmosome. J Clin Invest. 1990;86:1088–1094. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stanley J.R., Hawley-Nelson P., Yuspa S.H., Shevach E.M., Katz S.I. Characterization of bullous pemphigoid antigen: a unique basement membrane protein of stratified squamous epithelia. Cell. 1981;24:897–903. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

