The nucleus- and endoplasmic reticulum-targeted forms of protein tyrosine phosphatase 61F regulate Drosophila growth, life span, and fecundity
- PMID: 23339871
- PMCID: PMC3624282
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01411-12
The nucleus- and endoplasmic reticulum-targeted forms of protein tyrosine phosphatase 61F regulate Drosophila growth, life span, and fecundity
Abstract
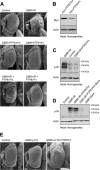
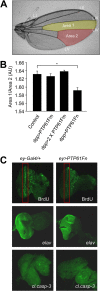
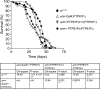
The protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) T cell PTP (TCPTP) and PTP1B share a high level of catalytic domain sequence and structural similarity yet display distinct differences in substrate recognition and function. Their noncatalytic domains contribute to substrate selectivity and function by regulating TCPTP nucleocytoplasmic shuttling and targeting PTP1B to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The Drosophila TCPTP/PTP1B orthologue PTP61F has two variants with identical catalytic domains that are differentially targeted to the ER and nucleus. Here we demonstrate that the PTP61F variants differ in their ability to negatively regulate insulin signaling in vivo, with the nucleus-localized form (PTP61Fn) being more effective than the ER-localized form (PTP61Fm). We report that PTP61Fm is reliant on the adaptor protein Dock to attenuate insulin signaling in vivo. Also, we show that the PTP61F variants differ in their capacities to regulate growth, with PTP61Fn but not PTP61Fm attenuating cellular proliferation. Furthermore, we generate a mutant lacking both PTP61F variants, which displays a reduction in median life span and a decrease in female fecundity, and show that both variants are required to rescue these mutant phenotypes. Our findings define the role of PTP61F in life span and fecundity and reinforce the importance of subcellular localization in mediating PTP function in vivo.
Figures



References
-
- Tonks NK. 2006. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: from genes, to function, to disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7:833–846 - PubMed
-
- Iversen LF, Moller KB, Pedersen AK, Peters GH, Petersen AS, Andersen HS, Branner S, Mortensen SB, Moller NP. 2002. Structure determination of T cell protein tyrosine phosphatase. J. Biol. Chem. 277:19982–19990 - PubMed
-
- Salmeen A, Andersen JN, Myers MP, Tonks NK, Barford D. 2000. Molecular basis for recognition and dephosphorylation of the activation segment of the insulin receptor by protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B. Mol. Cell 6:1401–1412 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
