TAF7: traffic controller in transcription initiation
- PMID: 23340207
- PMCID: PMC3644039
- DOI: 10.4161/trns.22842
TAF7: traffic controller in transcription initiation
Abstract
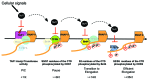
TAF7, a component of the TFIID complex, controls the first steps of transcription. It interacts with and regulates the enzymatic activities of transcription factors that regulate RNA polymerase II progression. Its diverse functions in transcription initiation are consistent with its essential role in cell proliferation.
Keywords: T cells; TAF7; differentiation; proliferation; transcriptional regulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TFIID component TAF7 functionally interacts with both TFIIH and P-TEFb.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Apr 8;105(14):5367-72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0801637105. Epub 2008 Apr 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18391197 Free PMC article.
-
TAF7: a possible transcription initiation check-point regulator.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jan 17;103(3):602-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510031103. Epub 2006 Jan 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16407123 Free PMC article.
-
The general transcription factor TAF7 is essential for embryonic development but not essential for the survival or differentiation of mature T cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 May;32(10):1984-97. doi: 10.1128/MCB.06305-11. Epub 2012 Mar 12. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22411629 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the RNA polymerase II pre-initiation complex by its associated coactivators.Nat Rev Genet. 2023 Nov;24(11):767-782. doi: 10.1038/s41576-023-00630-9. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Nat Rev Genet. 2023. PMID: 37532915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of transcription elongation by phosphorylation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Sep 13;1577(2):261-275. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4781(02)00457-8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12213657 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-374c-5p inhibits the development of breast cancer through TATA-box binding protein associated factor 7-mediated transcriptional regulation of DEP domain containing 1.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Sep;120(9):15360-15368. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28803. Epub 2019 Jun 4. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31162714 Free PMC article.
-
The nuclear transcription factor, TAF7, is a cytoplasmic regulator of protein synthesis.Sci Adv. 2021 Dec 10;7(50):eabi5751. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abi5751. Epub 2021 Dec 10. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 34890234 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of transcriptional initiation by RNA polymerase II across eukaryotic species.Elife. 2021 Sep 13;10:e67964. doi: 10.7554/eLife.67964. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34515029 Free PMC article.
-
Long Non-Coding RNAs in Atrial Fibrillation: Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes as a Model System.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 30;21(15):5424. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155424. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32751460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zooming in on Transcription Preinitiation.J Mol Biol. 2016 Jun 19;428(12):2581-2591. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.04.003. Epub 2016 Apr 8. J Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27067110 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
