Glucocorticoids reduce intracellular calcium concentration and protects neurons against glutamate toxicity
- PMID: 23340218
- PMCID: PMC4208294
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceca.2012.12.006
Glucocorticoids reduce intracellular calcium concentration and protects neurons against glutamate toxicity
Abstract
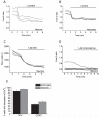
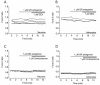
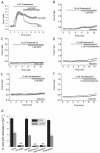
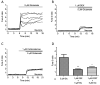
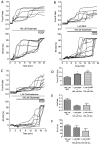
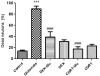
Glucocorticoids are steroid hormones which act through the glucocorticoid receptor. They regulate a wide variety of biological processes. Two glucocorticoids, the naturally occurring corticosterone and chemically produced dexamethasone, have been used to investigate the effect of glucocorticoids on Ca(2+)-signalling in cortical co-cultures of neurons and astrocytes. Dexamethasone and to a lesser degree corticosterone both induced a decrease in cytosolic Ca(2+) concentration in neurons and astrocytes. The effect of both compounds can be blocked by inhibition of the plasmamembrane ATPase, calmodulin and by application of a glucocorticoid receptor antagonist, while inhibition of NMDA receptors or the endoplasmic reticulum calcium pump had no effect. Glucocorticoid treatment further protects against detrimental calcium signalling and cell death by modulating the delayed calcium deregulation in response to glutamate toxicity. At the concentrations used dexamethasone and corticosterone did not show cell toxicity of their own. Thus, these results indicate that dexamethasone and corticosterone might be used for protection of the cells from calcium overload.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
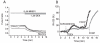
References
-
- Kim M, Lee G, Jung E, Choi K, Oh G, Jeung E. Dexamethasone differentially regulates renal and duodenal calcium-processing genes in calbindin-D9k and D28k knockout mice. Experimental Physiology. 2009;94:138–151. - PubMed
-
- Chen S, Wang X, Zhang X, Wang W, Liu D, Long Z, Dai W, Chen Q, Xu M, Zhou J. High-dose glucocorticoids induce decreases calcium in hypothalamus neurons via plasma membrane Ca2+ pumps. NeuroReport. 2011;22:660–663. - PubMed
-
- Reul JMHM, Bosch J.R.V.d., de ERK. Relative occupation of type 1 and type 2 corticosteroid receptors in rat brain following stress and dexamethasone treatment: functional implications. Journal of Endocrinology. 1987;115:459–467. - PubMed
-
- Beato M, Klug J. Steroid hormone receptors: an update. Human Reproduction Update. 2000;6:225–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

