Tyrosyl phosphorylated PAK1 regulates breast cancer cell motility in response to prolactin through filamin A
- PMID: 23340249
- PMCID: PMC3589676
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2012-1291
Tyrosyl phosphorylated PAK1 regulates breast cancer cell motility in response to prolactin through filamin A
Abstract
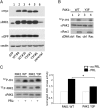
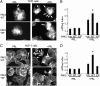
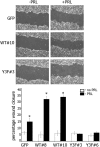
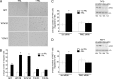
The p21-activated serine-threonine kinase (PAK1) is activated by small GTPase-dependent and -independent mechanisms and regulates cell motility. Both PAK1 and the hormone prolactin (PRL) have been implicated in breast cancer by numerous studies. We have previously shown that the PRL-activated tyrosine kinase JAK2 (Janus tyrosine kinase 2) phosphorylates PAK1 in vivo and identified tyrosines (Tyr) 153, 201, and 285 in the PAK1 molecule as sites of JAK2 tyrosyl phosphorylation. Here, we have used human breast cancer T47D cells stably overexpressing PAK1 wild type or PAK1 Y3F mutant in which Tyr(s) 153, 201, and 285 were mutated to phenylalanines to demonstrate that phosphorylation of these three tyrosines are required for maximal PRL-dependent ruffling. In addition, phosphorylation of these three tyrosines is required for increased migration of T47D cells in response to PRL as assessed by two independent motility assays. Finally, we show that PAK1 phosphorylates serine (Ser) 2152 of the actin-binding protein filamin A to a greater extent when PAK1 is tyrosyl phosphorylated by JAK2. Down-regulation of PAK1 or filamin A abolishes the effect of PRL on cell migration. Thus, our data presented here bring some insight into the mechanism of PRL-stimulated motility of breast cancer cells.
Figures
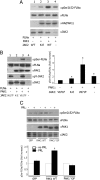
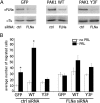
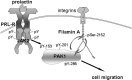
Similar articles
-
PAK1 regulates breast cancer cell invasion through secretion of matrix metalloproteinases in response to prolactin and three-dimensional collagen IV.Mol Endocrinol. 2013 Jul;27(7):1048-64. doi: 10.1210/me.2012-1322. Epub 2013 Jun 6. Mol Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23744893 Free PMC article.
-
Adapter protein SH2B1beta binds filamin A to regulate prolactin-dependent cytoskeletal reorganization and cell motility.Mol Endocrinol. 2011 Jul;25(7):1231-43. doi: 10.1210/me.2011-0056. Epub 2011 May 12. Mol Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21566085 Free PMC article.
-
Prolactin-induced PAK1 tyrosyl phosphorylation promotes FAK dephosphorylation, breast cancer cell motility, invasion and metastasis.BMC Cell Biol. 2016 Aug 20;17(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s12860-016-0109-5. BMC Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27542844 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosyl phosphorylated serine-threonine kinase PAK1 is a novel regulator of prolactin-dependent breast cancer cell motility and invasion.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;846:97-137. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-12114-7_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 25472536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of the PRL-PAK1 Pathway in Cancer Cell Migration.Cancer Diagn Progn. 2023 Jan 3;3(1):17-25. doi: 10.21873/cdp.10174. eCollection 2023 Jan-Feb. Cancer Diagn Progn. 2023. PMID: 36632591 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PAK1 translocates into nucleus in response to prolactin but not to estrogen.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Apr 22;473(1):206-211. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.03.079. Epub 2016 Mar 19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27003261 Free PMC article.
-
The SH2 domain and kinase activity of JAK2 target JAK2 to centrosome and regulate cell growth and centrosome amplification.PLoS One. 2022 Jan 28;17(1):e0261098. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261098. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35089929 Free PMC article.
-
Prolactin Signaling Stimulates Invasion via Na(+)/H(+) Exchanger NHE1 in T47D Human Breast Cancer Cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2016 Jul;30(7):693-708. doi: 10.1210/me.2015-1299. Epub 2016 May 13. Mol Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27176613 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating PAK1: Accessory Proteins as Promising Therapeutic Targets.Biomolecules. 2025 Feb 7;15(2):242. doi: 10.3390/biom15020242. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PAK1 regulates breast cancer cell invasion through secretion of matrix metalloproteinases in response to prolactin and three-dimensional collagen IV.Mol Endocrinol. 2013 Jul;27(7):1048-64. doi: 10.1210/me.2012-1322. Epub 2013 Jun 6. Mol Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23744893 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goffin V, Bernichtein S, Touraine P, Kelly PA. Development and potential clinical uses of human prolactin receptor antagonists. Endocr Rev. 2005;26:400–422 - PubMed
-
- Bernichtein S, Touraine P, Goffin V. New concepts in prolactin biology. J Endocrinol. 2010;206:1–11 - PubMed
-
- DaSilva L, Rui H, Erwin RA, Howard OM, Kirken RA, Malabarba MG, Hackett RH, Larner AC, Farrar WL. Prolactin recruits STAT1, STAT3 and STAT5 independent of conserved receptor tyrosines TYR402, TYR479, TYR515 and TYR580. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1996;117:131–140 - PubMed
-
- Schaber JD, Fang H, Xu J, Grimley PM, Rui H. Prolactin activates Stat1 but does not antagonize Stat1 activation and growth inhibition by type I interferons in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1998;58:1914–1919 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

