One size does not fit all: the oligomeric states of αB crystallin
- PMID: 23340341
- PMCID: PMC3865782
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.01.021
One size does not fit all: the oligomeric states of αB crystallin
Abstract
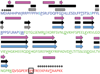
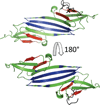
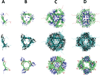
Small Heat Shock Proteins (sHSPs) are a diverse family of molecular chaperones that delay protein aggregation through interactions with non-native and aggregate-prone protein states. This function has been shown to be important to cellular viability and sHSP function/dysfunction is implicated in many diseases, including Alzheimer's and Alexander disease. Though their gene products are small, many sHSPs assemble into a distribution of large oligomeric states that undergo dynamic subunit exchange. These inherent properties present significant experimental challenges for characterizing sHSP oligomers. Of the human sHSPs, αB crystallin is a paradigm example of sHSP oligomeric properties. Advances in our understanding of sHSP structure, oligomeric distribution, and dynamics have prompted the proposal of several models for the oligomeric states of αB. The aim of this review is to highlight characteristics of αB crystallin (αB) that are key to understanding its structure and function. The current state of knowledge, existing models, and outstanding questions that remain to be addressed are presented.
Copyright © 2013 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Single-molecule observations of human small heat shock proteins in complex with aggregation-prone client proteins.Biochem J. 2025 May 6;482(9):413-432. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20240473. Biochem J. 2025. PMID: 40241479 Free PMC article.
-
The function of the beta3 interactive domain in the small heat shock protein and molecular chaperone, human alphaB crystallin.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2006 Summer;11(2):187-97. doi: 10.1379/csc-186.1. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2006. PMID: 16817325 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Cu2+-mediated generation of reactive oxygen species by the small heat shock protein αB-crystallin: the relative contributions of the N- and C-terminal domains.Free Radic Biol Med. 2011 Aug 1;51(3):755-62. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.05.021. Epub 2011 May 26. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011. PMID: 21658443
-
The multifaceted nature of αB-crystallin.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2020 Jul;25(4):639-654. doi: 10.1007/s12192-020-01098-w. Epub 2020 May 7. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2020. PMID: 32383140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamical structure of αB-crystallin.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2014 Jul;115(1):11-20. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2014.03.003. Epub 2014 Mar 24. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24674783 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of αA- and αB-crystallins via phosphorylation in cellular homeostasis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Nov;72(21):4127-37. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1996-x. Epub 2015 Jul 26. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26210153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Mutated MYOT and CRYAB Genes Cause a Myopathic Phenotype in Zebrafish.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 14;24(14):11483. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411483. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511242 Free PMC article.
-
Single-molecule observations of human small heat shock proteins in complex with aggregation-prone client proteins.Biochem J. 2025 May 6;482(9):413-432. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20240473. Biochem J. 2025. PMID: 40241479 Free PMC article.
-
It takes a dimer to tango: Oligomeric small heat shock proteins dissociate to capture substrate.J Biol Chem. 2018 Dec 21;293(51):19511-19521. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005421. Epub 2018 Oct 22. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30348902 Free PMC article.
-
Small heat-shock proteins: important players in regulating cellular proteostasis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Feb;72(3):429-451. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1754-5. Epub 2014 Oct 29. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25352169 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Haslbeck M, Franzmann T, Weinfurtner D, Buchner J, Buchner J. Some like it hot: the structure and function of small heat-shock proteins. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005;10:842–846. - PubMed
-
- Vicart P, Caron A, Guicheney P, Li Z, Prévost M, Faure A, Chateau D, Chapon F, Tomé F, Dupret J, Paulin D, Fardeau M. A missense mutation in the αB-crystallin chaperone gene causes a desmin-related myopathy. Nat Genet. 1998;20:92–95. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein LE, Muffat JA, Cherny RA, Moir RD, Ericsson MH, Huang X, Mavros C, Coccia JA, Faget KY, Fitch KA, Masters CL, Tanzi RE, Jr, LTC, Bush AI. Cytosolic β-amyloid deposition and supranuclear cataracts in lenses from people with Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet. 2003;361:1258–1265. - PubMed
-
- Kato K, Inaguma Y, Ito H, Iida K, Iwamoto I, Kamei K, Ochi N, Ohta H, Kishikawa M. Ser-59 is the major phosphorylation site in aBcrystallin accumulated in the brains of patients with Alexander’s disease. J Neurochem. 2001;76:730–736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

