MicroRNA-30c inhibits human breast tumour chemotherapy resistance by regulating TWF1 and IL-11
- PMID: 23340433
- PMCID: PMC3723106
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms2393
MicroRNA-30c inhibits human breast tumour chemotherapy resistance by regulating TWF1 and IL-11
Abstract
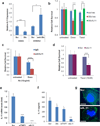
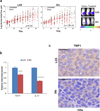
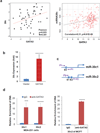
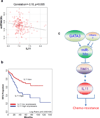
Chemotherapy resistance frequently drives tumour progression. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms are poorly characterized. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition has been shown to correlate with therapy resistance, but the functional link and signalling pathways remain to be elucidated. Here we report that microRNA-30c, a human breast tumour prognostic marker, has a pivotal role in chemoresistance by a direct targeting of the actin-binding protein twinfilin 1, which promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. An interleukin-6 family member, interleukin-11 is identified as a secondary target of twinfilin 1 in the microRNA-30c signalling pathway. Expression of microRNA-30c inversely correlates with interleukin-11 expression in primary breast tumours and low interleukin-11 correlates with relapse-free survival in breast cancer patients. Our study demonstrates that microRNA-30c is transcriptionally regulated by GATA3 in breast tumours. Identification of a novel microRNA-mediated pathway that regulates chemoresistance in breast cancer will facilitate the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
Figures
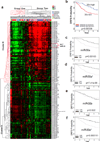
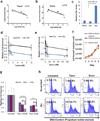
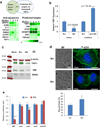
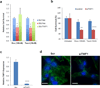
References
-
- Lu J, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005;435:834–838. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Fabian MR, Sonenberg N, Filipowicz W. Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 2010;79:351–379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 GM061393/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA075136/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA058223/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA139278/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 014599/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK070103-05/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA100225/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA159066/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 CA139160/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA125183/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1K12CA139160-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024999/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014599/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01GM61393/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K99 CA160638/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA126524/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T90 DK070103/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1R21CA159066/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 CA160638-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA104987/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA139490/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5-P50-CA58223-17/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 CA160638/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA154209/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50CA125183-05/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

