Candida parapsilosis is a significant neonatal pathogen: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 23340551
- PMCID: PMC3681839
- DOI: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3182863a1c
Candida parapsilosis is a significant neonatal pathogen: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Candida is the third most common cause of late-onset neonatal sepsis in infants born at <1500 g. Candida parapsilosis infections are increasingly reported in preterm neonates in association with indwelling catheters.
Methods: We systematically reviewed neonatal literature and synthesized data pertaining to percentage of C. parapsilosis infections and mortality by meta-analyses. We also reviewed risk factors, virulence determinants, antimicrobial susceptibility patterns and outlined clinical management strategies.
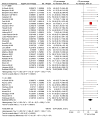
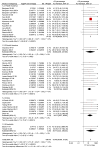
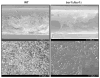
Results: C. parapsilosis infections comprised 33.47% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 30.02, 37.31) of all neonatal Candida infections. C. parapsilosis rates were similar in studies performed before the year 2000, 33.53% (95% CI: 30.06, 37.40) (28 studies), to those after 2000, 27.00% (95% CI: 8.25, 88.37) (8 studies). The mortality due to neonatal C. parapsilosis infections was 10.02% (95% CI: 7.66, 13.12). Geographical variations in C. parapsilosis infections included a low incidence in Europe and higher incidence in North America and Australia. Biofilm formation was a significant virulence determinant and predominant risk factors for C. parapsilosis infections were prematurity, prior colonization and catheterization. Amphotericin B remains the antifungal drug of choice and combination therapy with caspofungin or other echinocandins may be considered in resistant cases.
Conclusion: C. parapsilosis is a significant neonatal pathogen, comprises a third of all Candida infections and is associated with 10% mortality. Availability of tools for genetic manipulation of this organism will identify virulence determinants and organism characteristics that may explain predilection for preterm neonates. Strategies to prevent horizontal transmission in the neonatal unit are paramount in decreasing infection rates.
Figures
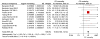
References
-
- Stoll BJ, Hansen N, Fanaroff AA, et al. Late-onset sepsis in very low birth weight neonates: the experience of the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics. 2002;110:285–291. - PubMed
-
- Wisplinghoff H, Bischoff T, Tallent SM, et al. Nosocomial bloodstream infections in US hospitals: analysis of 24,179 cases from a prospective nationwide surveillance study. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:309–317. - PubMed
-
- Brito LR, Guimaraes T, Nucci M, et al. Clinical and microbiological aspects of candidemia due to Candida parapsilosis in Brazilian tertiary care hospitals. Med Mycol. 2006;44:261–266. - PubMed
-
- Krcmery V, Barnes AJ. Non-albicans Candida spp. causing fungaemia: pathogenicity and antifungal resistance. J Hosp Infect. 2002;50:243–260. - PubMed

