Sex-specific clines support incipient speciation in a common European mammal
- PMID: 23340600
- PMCID: PMC3607112
- DOI: 10.1038/hdy.2012.124
Sex-specific clines support incipient speciation in a common European mammal
Abstract
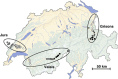
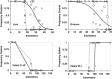
Hybrid zones provide excellent opportunities to study processes and mechanisms underlying reproductive isolation and speciation. Here we investigated sex-specific clines of molecular markers in hybrid zones of morphologically cryptic yet genetically highly-diverged evolutionary lineages of the European common vole (Microtus arvalis). We analyzed the position and width of four secondary contact zones along three independent transects in the region of the Alps using maternally (mitochondrial DNA) and paternally (Y-chromosome) inherited genetic markers. Given male-biased dispersal in the common vole, a selectively neutral secondary contact would show broader paternal marker clines than maternal ones. In a selective case, for example, involving a form of Haldane's rule, Y-chromosomal clines would not be expected to be broader than maternal markers because they are transmitted by the heterogametic sex and thus gene flow would be restricted. Consistent with the selective case, paternal clines were significantly narrower or at most equal in width to maternal clines in all contact zones. In addition, analyses using maximum likelihood cline-fitting detected a shift of paternal relative to maternal clines in three of four contact zones. These patterns suggest that processes at the contact zones in the common vole are not selectively neutral, and that partial reproductive isolation is already established between these evolutionary lineages. We conclude that hybrid zone movement, sexual selection and/or genetic incompatibilities are likely associated with an unusual unidirectional manifestation of Haldane's rule in this common European mammal.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structure and dynamics of hybrid zones at different stages of speciation in the common vole (Microtus arvalis).Mol Ecol. 2014 Feb;23(3):673-87. doi: 10.1111/mec.12613. Mol Ecol. 2014. PMID: 24450982
-
Speciation in Western Scrub-Jays, Haldane's rule, and genetic clines in secondary contact.BMC Evol Biol. 2014 Jun 17;14:135. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-14-135. BMC Evol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24938753 Free PMC article.
-
Tracing reinforcement through asymmetrical partner preference in the European common vole Microtus arvalis.BMC Evol Biol. 2015 Aug 25;15:170. doi: 10.1186/s12862-015-0455-5. BMC Evol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26303785 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating genomic signatures of "the large X-effect" during complex speciation.Mol Ecol. 2018 Oct;27(19):3822-3830. doi: 10.1111/mec.14777. Epub 2018 Jul 16. Mol Ecol. 2018. PMID: 29940087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Avian Introgression Patterns are Consistent With Haldane's Rule.J Hered. 2022 Jul 23;113(4):363-370. doi: 10.1093/jhered/esac005. J Hered. 2022. PMID: 35134952 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple infections of rodents with zoonotic pathogens in Austria.Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014 Jul;14(7):467-75. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2013.1504. Epub 2014 Jun 10. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014. PMID: 24915446 Free PMC article.
-
Introgressive replacement of natives by invading Arion pest slugs.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 2;7(1):14908. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14619-y. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29097725 Free PMC article.
-
Asymmetric allelic introgression across a hybrid zone of the coal tit (Periparus ater) in the central Himalayas.Ecol Evol. 2021 Nov 24;11(23):17332-17351. doi: 10.1002/ece3.8369. eCollection 2021 Dec. Ecol Evol. 2021. PMID: 34938512 Free PMC article.
-
Host genetic factors associated with the range limit of a European hantavirus.Mol Ecol. 2022 Jan;31(1):252-265. doi: 10.1111/mec.16211. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Mol Ecol. 2022. PMID: 34614264 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide support for incipient Tula hantavirus species within a single rodent host lineage.Virus Evol. 2024 Jan 5;10(1):veae002. doi: 10.1093/ve/veae002. eCollection 2024. Virus Evol. 2024. PMID: 38361825 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baird SJE, Ribas A, Macholán M, Albrecht T, Piálek J, Goüy de Bellocq J. Where are the wormy mice? A reexamination of hybrid parasitism in the European House mouse hybrid zone. Evolution. 2012;66:2757–2772. - PubMed
-
- Barton NH, Baird SJE.2002. ANALYSE, Version 1.3: Freeware: available from http://helios.bto.edsac.uk/evolgen/Mac/Analyse .
-
- Barton NH, Hewitt GM. Analysis of hybrid zones. Annu Rev Ecol Syst. 1985;16:113–148.
-
- Barton NH, Hewitt GM. Adaptation, speciation and hybrid zones. Nature. 1989;341:497–503. - PubMed
-
- Bastos-Silveira C, Santos SM, Monarca R, Mathias ML, Heckel G. Deep mitochondrial introgression and hybridization between ecologically divergent vole species. Mol Ecol. 2012;21:5309–5323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

