A validated ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the quantification of polymyxin B in mouse serum and epithelial lining fluid: application to pharmacokinetic studies
- PMID: 23341128
- PMCID: PMC3625435
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dks536
A validated ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the quantification of polymyxin B in mouse serum and epithelial lining fluid: application to pharmacokinetic studies
Abstract
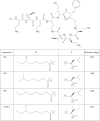
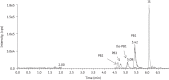
Objectives: A rapid, sensitive and robust ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) method was developed for the quantification of four major polymyxin B components (polymyxin B1, polymyxin B2, polymyxin B3 and isoleucine-polymyxin B1) in serum and epithelial lining fluid (ELF) samples.
Methods: A Waters Acquity UPLC HSS C18 column was used with 0.1% formic acid in water/acetonitrile as mobile phases. Analysis was performed in a positive ionization mode with multiple-reactions monitoring scan type. Five percent trichloroacetic acid was used to precipitate proteins in biological samples and to increase the sensitivity of detection.
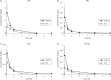
Results: Our results showed a linear concentration range of 0.0065-3.2 mg/L for all the major polymyxin B components in both serum and ELF, respectively; the interday variation was <10% and the accuracy was 88%-115%. The validated method was used to characterize the pharmacokinetics (serum and ELF) of polymyxin B in mice.
Conclusions: This is the first report, to date, examining the individual pharmacokinetics of various polymyxin B components in mice. Our results revealed no considerable differences in clearances among the components. The limited exposure of polymyxin B in ELF observed was consistent with the less favourable efficacy of polymyxin B reported for the treatment of pulmonary infections. This method can be used to further examine the pharmacokinetics of polymyxin B in a variety of clinical and experimental settings.
Figures

References
-
- Gales AC, Jones RN, Sader HS. Global assessment of the antimicrobial activity of polymyxin B against 54 731 clinical isolates of Gram-negative bacilli: report from the SENTRY antimicrobial surveillance programme (2001–2004) Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006;12:315–21. - PubMed
-
- Pastewski AA, Caruso P, Parris AR, et al. Parenteral polymyxin B use in patients with multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteremia and urinary tract infections: a retrospective case series. Ann Pharmacother. 2008;42:1177–87. - PubMed
-
- Bratu S, Quale J, Cebular S, et al. Multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Brooklyn, New York: molecular epidemiology and in vitro activity of polymyxin B. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2005;24:196–201. - PubMed
-
- Shoji J, Hinoo H, Wakisaka Y, et al. Isolation of two new polymyxin group antibiotics. (Studies on antibiotics from the genus Bacillus. XX) J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977;30:1029–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

