The four and a half LIM-domain 2 controls early cardiac cell commitment and expansion via regulating β-catenin-dependent transcription
- PMID: 23341242
- PMCID: PMC3744766
- DOI: 10.1002/stem.1332
The four and a half LIM-domain 2 controls early cardiac cell commitment and expansion via regulating β-catenin-dependent transcription
Abstract
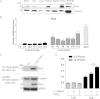
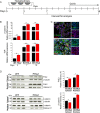
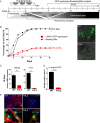
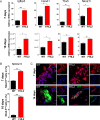
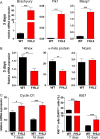
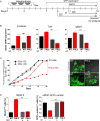
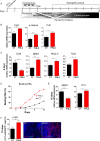
The multiphasic regulation of the Wnt/β-catenin canonical pathway is essential for cardiogenesis in vivo and in vitro. To achieve tight regulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling, tissue- and cell-specific coactivators and repressors need to be recruited. The identification of such factors may help to elucidate mechanisms leading to enhanced cardiac differentiation efficiency in vitro as well as promote regeneration in vivo. Using a yeast-two-hybrid screen, we identified four-and-a-half-LIM-domain 2 (FHL2) as a cardiac-specific β-catenin interaction partner and activator of Wnt/β-catenin-dependent transcription. We analyzed the role of this interaction for early cardiogenesis in an in vitro model by making use of embryoid body cultures from mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs). In this model, stable FHL2 gain-of-function promoted mesodermal cell formation and cell proliferation while arresting cardiac differentiation in an early cardiogenic mesodermal progenitor state. Mechanistically, FHL2 overexpression enhanced nuclear accumulation of β-catenin and activated Wnt/β-catenin-dependent transcription leading to sustained upregulation of the early cardiogenic gene Igfbp5. In an alternative P19 cell model, transient FHL2 overexpression led to early activation of Wnt/β-catenin-dependent transcription, but not sustained high-level of Igfbp5 expression. This resulted in enhanced cardiogenesis. We propose that early Wnt/β-catenin-dependent transcriptional activation mediated by FHL2 is important for the transition to and expansion of early cardiogenic mesodermal cells. Collectively, our findings offer mechanistic insight into the early cardiogenic code and may be further exploited to enhance cardiac progenitor cell activity in vitro and in vivo.
Copyright © 2013 AlphaMed Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
FHL2 mediates dexamethasone-induced mesenchymal cell differentiation into osteoblasts by activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling-dependent Runx2 expression.FASEB J. 2008 Nov;22(11):3813-22. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-106302. Epub 2008 Jul 24. FASEB J. 2008. PMID: 18653765
-
Wnt/β-catenin and Bmp signals control distinct sets of transcription factors in cardiac progenitor cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 3;109(27):10921-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1121236109. Epub 2012 Jun 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22711842 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of FHL2 in fibroblasts attenuates fibroblasts activation and kidney fibrosis via restraining TGF-β1-induced Wnt/β-catenin signaling.J Mol Med (Berl). 2020 Feb;98(2):291-307. doi: 10.1007/s00109-019-01870-1. Epub 2020 Jan 11. J Mol Med (Berl). 2020. PMID: 31927599
-
Unlocking the secrets of Cardiac development and function: the critical role of FHL2.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Apr;480(4):2143-2157. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05142-6. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39466483 Review.
-
The roles of FHL2 in cancer.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Nov;23(7):3113-3124. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01076-3. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 37103649 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Maturation of Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes Promoted by Mechanical Stretch.Med Sci Monit. 2021 Aug 12;27:e931063. doi: 10.12659/MSM.931063. Med Sci Monit. 2021. PMID: 34381009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
De novo HAPLN1 expression hallmarks Wnt-induced stem cell and fibrogenic networks leading to aggressive human hepatocellular carcinomas.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 28;7(26):39026-39043. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9346. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27191501 Free PMC article.
-
Intrauterine Programming of Diabetes Induced Cardiac Embryopathy.Diabetes Obes Int J. 2019;4(3):202. Epub 2019 May 6. Diabetes Obes Int J. 2019. PMID: 32537569 Free PMC article.
-
A novel genomic signature with translational significance for human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015 Feb;52(2):217-31. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0310OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25029475 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brembeck FH, Rosario M, Birchmeier W. Balancing cell adhesion and Wnt signaling, the key role of beta-catenin. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006;16:51–59. - PubMed
-
- Cadigan KM. Wnt-beta-catenin signaling. Curr Biol. 2008;18:R943–R947. - PubMed
-
- Gordon MD, Nusse R. Wnt signaling: Multiple pathways, multiple receptors, and multiple transcription factors. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:22429–22433. - PubMed
-
- Tam PP, Loebel DA. Gene function in mouse embryogenesis: Get set for gastrulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:368–381. - PubMed
-
- Grapin-Botton A, Constam D. Evolution of the mechanisms and molecular control of endoderm formation. Mech Dev. 2007;124:253–278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

