Device to monitor sock use in people using prosthetic limbs: technical report
- PMID: 23341315
- PMCID: PMC4439930
- DOI: 10.1682/jrrd.2011.09.0169
Device to monitor sock use in people using prosthetic limbs: technical report
Abstract
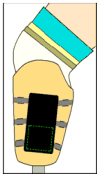
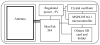
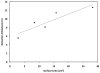
A device using radio frequency identification (RFID) technology was developed to continuously monitor sock use in people who use prosthetic limbs. RFID tags were placed on prosthetic socks worn by subjects with transtibial limb loss, and a high-frequency RFID reader and antenna were placed in a portable unit mounted to the outside of the prosthetic socket. Bench testing showed the device to have a maximum read range between 5.6 cm and 12.7 cm, depending on the RFID tag used. Testing in a laboratory setting on three participants with transtibial amputation showed that the device correctly monitored sock presence during sitting, standing, and walking activity when one or two socks were worn but was less reliable when more socks were used. Accurate detection was sensitive to orientation of the tag relative to the reader, presence of carbon fiber in the prosthetic socket, pistoning of the limb in the socket, and overlap among the tags. Use of ultra-high-frequency RFID may overcome these limitations. With improvements, the technology may prove useful to practitioners prescribing volume accommodation strategies for patients by providing information about sock use between clinical visits, including timing and consistency of daily sock-ply changes.
Figures

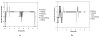
References
-
- Highsmith JM, Kahle JT. Prosthetic socks: simple, low-cost, helpful ways to protect your skin. Motion. 2006;16(2)
-
- Uddin J, Reaz MBI, Hasan MA, Nordin AN, Ibrahimy MI, Ali MAM. UHF RFID antenna architectures and applications. Sci Res Essays. 2010;5(10):1033–51.
-
- Nikitin PV, Rao KVS, Lazar S. An overview of near field UHF RFID. IEEE International Conference on RFID; 2007; pp. 167–74.
-
- MatWeb. Material Property Data. 2011 Sep 12; MatWeb.com.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
