β-Arrestin recruitment and G protein signaling by the atypical human chemokine decoy receptor CCX-CKR
- PMID: 23341447
- PMCID: PMC3591626
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.406108
β-Arrestin recruitment and G protein signaling by the atypical human chemokine decoy receptor CCX-CKR
Abstract
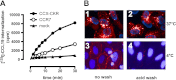
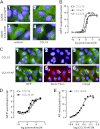
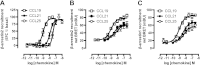
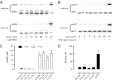
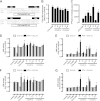
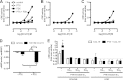
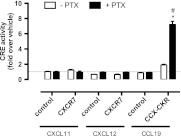
Chemokine receptors form a large subfamily of G protein-coupled receptors that predominantly activate heterotrimeric Gi proteins and are involved in immune cell migration. CCX-CKR is an atypical chemokine receptor with high affinity for CCL19, CCL21, and CCL25 chemokines, but is not known to activate intracellular signaling pathways. However, CCX-CKR acts as decoy receptor and efficiently internalizes these chemokines, thereby preventing their interaction with other chemokine receptors, like CCR7 and CCR9. Internalization of fluorescently labeled CCL19 correlated with β-arrestin2-GFP translocation. Moreover, recruitment of β-arrestins to CCX-CKR in response to CCL19, CCL21, and CCL25 was demonstrated using enzyme-fragment complementation and bioluminescence resonance energy transfer methods. To unravel why CCX-CKR is unable to activate Gi signaling, CCX-CKR chimeras were constructed by substituting its intracellular loops with the corresponding CCR7 or CCR9 domains. The signaling properties of chimeric CCX-CKR receptors were characterized using a cAMP-responsive element (CRE)-driven reporter gene assay. Unexpectedly, wild type CCX-CKR and a subset of the chimeras induced an increase in CRE activity in response to CCL19, CCL21, and CCL25 in the presence of the Gi inhibitor pertussis toxin. CCX-CKR signaling to CRE required an intact DRY motif. These data suggest that inactive Gi proteins impair CCX-CKR signaling most likely by hindering the interaction of this receptor with pertussis toxin-insensitive G proteins that transduce signaling to CRE. On the other hand, recruitment of the putative signaling scaffold β-arrestin to CCX-CKR in response to chemokines might allow activation of yet to be identified signal transduction pathways.
Figures

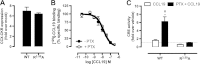
Similar articles
-
ACKR4 Recruits GRK3 Prior to β-Arrestins but Can Scavenge Chemokines in the Absence of β-Arrestins.Front Immunol. 2020 Apr 22;11:720. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00720. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32391018 Free PMC article.
-
The chemokine receptor CCX-CKR mediates effective scavenging of CCL19 in vitro.Eur J Immunol. 2006 Jul;36(7):1904-16. doi: 10.1002/eji.200535716. Eur J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16791897
-
CCL20 is a novel ligand for the scavenging atypical chemokine receptor 4.J Leukoc Biol. 2020 Jun;107(6):1137-1154. doi: 10.1002/JLB.2MA0420-295RRR. J Leukoc Biol. 2020. PMID: 32533638
-
Common and biased signaling pathways of the chemokine receptor CCR7 elicited by its ligands CCL19 and CCL21 in leukocytes.J Leukoc Biol. 2016 Jun;99(6):869-82. doi: 10.1189/jlb.2MR0815-380R. Epub 2016 Jan 4. J Leukoc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26729814 Review.
-
A myriad of functions and complex regulation of the CCR7/CCL19/CCL21 chemokine axis in the adaptive immune system.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013 Jun;24(3):269-83. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.03.001. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013. PMID: 23587803 Review.
Cited by
-
GPR18 undergoes a high degree of constitutive trafficking but is unresponsive to N-Arachidonoyl Glycine.PeerJ. 2016 Mar 21;4:e1835. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1835. eCollection 2016. PeerJ. 2016. PMID: 27018161 Free PMC article.
-
The Viral G Protein-Coupled Receptor ORF74 Hijacks β-Arrestins for Endocytic Trafficking in Response to Human Chemokines.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 20;10(4):e0124486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124486. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25894435 Free PMC article.
-
The Ion Channel and GPCR Toolkit of Brain Capillary Pericytes.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Dec 18;14:601324. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.601324. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33390906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral G Protein-Coupled Receptors Encoded by β- and γ-Herpesviruses.Annu Rev Virol. 2022 Sep 29;9(1):329-351. doi: 10.1146/annurev-virology-100220-113942. Epub 2022 Jun 7. Annu Rev Virol. 2022. PMID: 35671566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutant mice lacking alternatively spliced p53 isoforms unveil Ackr4 as a male-specific prognostic factor in Myc-driven B-cell lymphomas.Elife. 2024 Sep 19;13:RP92774. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92774. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39298333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O'Hayre M., Salanga C. L., Handel T. M., Allen S. J. (2008) Chemokines and cancer. Migration, intracellular signalling and intercellular communication in the microenvironment. Biochem. J. 409, 635–649 - PubMed
-
- Gosling J., Dairaghi D. J., Wang Y., Hanley M., Talbot D., Miao Z., Schall T. J. (2000) Cutting edge. Identification of a novel chemokine receptor that binds dendritic cell- and T cell-active chemokines including ELC, SLC, and TECK. J. Immunol. 164, 2851–2856 - PubMed
-
- Förster R., Davalos-Misslitz A. C., Rot A. (2008) CCR7 and its ligands. Balancing immunity and tolerance. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8, 362–371 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

