Responsiveness to a physiological regimen of GnRH therapy and relation to genotype in women with isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
- PMID: 23341491
- PMCID: PMC3565114
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2012-3294
Responsiveness to a physiological regimen of GnRH therapy and relation to genotype in women with isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
Abstract
Context: Isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (IHH) is caused by defective GnRH secretion or action resulting in absent or incomplete pubertal development and infertility. Most women with IHH ovulate with physiological GnRH replacement, implicating GnRH deficiency as the etiology. However, a subset does not respond normally, suggesting the presence of defects at the pituitary or ovary.
Objectives: The objective of the study was to unmask pituitary or ovarian defects in IHH women using a physiological regimen of GnRH replacement, relating these responses to genes known to cause IHH.
Design, setting, and subjects: This study is a retrospective analysis of 37 IHH women treated with iv pulsatile GnRH (75 ng/kg per bolus).
Main outcome measures: Serum gonadotropin and sex steroid levels were measured, and 14 genes implicated in IHH were sequenced.
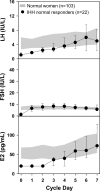
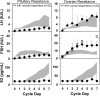
Results: During their first cycle of GnRH replacement, normal cycles were recreated in 60% (22 of 37) of IHH women. Thirty percent of women (12 of 37) demonstrated an attenuated gonadotropin response, indicating pituitary resistance, and 10% (3 of 37) exhibited an exaggerated FSH response, consistent with ovarian resistance. Mutations in CHD7, FGFR1, KAL1, TAC3, and TACR3 were documented in IHH women with normal cycles, whereas mutations were identified in GNRHR, PROKR2, and FGFR1 in those with pituitary resistance. Women with ovarian resistance were mutation negative.
Conclusions: Although physiological replacement with GnRH recreates normal menstrual cycle dynamics in most IHH women, hypogonadotropic responses in the first week of treatment identify a subset of women with pituitary dysfunction, only some of whom have mutations in GNRHR. IHH women with hypergonadotropic responses to GnRH replacement, consistent with an additional ovarian defect, did not have mutations in genes known to cause IHH, similar to our findings in a subset of IHH men with evidence of an additional testicular defect.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00383656.
Figures
References
-
- Martin K, Santoro N, Hall J, Filicori M, Wierman M, Crowley WF., Jr Clinical review 15: management of ovulatory disorders with pulsatile gonadotropin-releasing hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990;71(5):1081A–1081G - PubMed
-
- Seminara SB, Beranova M, Oliveira LM, Martin KA, Crowley WF, Jr, Hall JE. Successful use of pulsatile gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) for ovulation induction and pregnancy in a patient with GnRH receptor mutations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85(2):556–562 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- R01 HD042708/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD015788/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HD067388/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HD073304/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HD062315/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5F32 HD062315/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD42708/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD043341/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD028138/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-01066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

