Serum cystatin C is a major predictor of vancomycin clearance in a population pharmacokinetic analysis of patients with normal serum creatinine concentrations
- PMID: 23341711
- PMCID: PMC3546104
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.1.48
Serum cystatin C is a major predictor of vancomycin clearance in a population pharmacokinetic analysis of patients with normal serum creatinine concentrations
Abstract
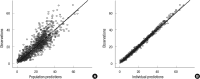
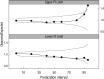
We developed a population pharmacokinetic model of vancomycin by integrating the effects of cystatin C and other demographic factors in a large population of Korean patients with normal serum creatinine concentrations to elucidate the precise role of serum cystatin C concentrations in the prediction of vancomycin clearance. A population pharmacokinetic model of vancomycin was developed using NONMEM software from a total of 1,373 vancomycin concentration measurements in 678 patients whose serum creatinine concentrations were lower than 1.2 mg/dL. Covariate selection revealed that cystatin C was the most influential factor and had negative influence ((-0.78)) in the relationship. Total body weight, sex, age, and serum creatinine were also significantly correlated with the clearance. The estimated intersubject variabilities of clearance and volume of distribution were 24.7% and 25.1%, respectively. A 14-fold difference in predicted trough concentrations was observed according to only cystatin C concentrations in a population of simulated individuals with median demographic characteristics. The use of serum cystatin C as marker of vancomycin clearance for more accurate predictions of serum vancomycin concentrations could be useful, particularly among patients with normal serum creatinine concentrations.
Keywords: Cystatin C; NONMEM; Pharmacokinetics; TDM; Vancomycin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of the Predictive Performance Between Cystatin C and Serum Creatinine by Vancomycin via a Population Pharmacokinetic Models: A Prospective Study in a Chinese Population.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2020 Feb;45(1):135-149. doi: 10.1007/s13318-019-00578-4. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2020. PMID: 31541402
-
Serum cystatin C predicts vancomycin trough levels better than serum creatinine in hospitalized patients: a cohort study.Crit Care. 2014 May 29;18(3):R110. doi: 10.1186/cc13899. Crit Care. 2014. PMID: 24887089 Free PMC article.
-
Serum cystatin C for the prediction of glomerular filtration rate with regard to the dose adjustment of amikacin, gentamicin, tobramycin, and vancomycin.Ther Drug Monit. 2006 Jun;28(3):326-31. doi: 10.1097/01.ftd.0000211805.89440.3d. Ther Drug Monit. 2006. PMID: 16778715
-
Prediction of the Renal Elimination of Drugs With Cystatin C vs Creatinine: A Systematic Review.Mayo Clin Proc. 2019 Mar;94(3):500-514. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.08.002. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Mayo Clin Proc. 2019. PMID: 30713050
-
Predictive performance of reported population pharmacokinetic models of vancomycin in Chinese adult patients.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2013 Dec;38(6):480-9. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12092. Epub 2013 Sep 5. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2013. PMID: 24033587 Review.
Cited by
-
Vancomycin Population Pharmacokinetic Models in Non- Critically Ill Adults Patients: a scoping review.F1000Res. 2025 Mar 6;11:1513. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.128260.2. eCollection 2022. F1000Res. 2025. PMID: 40124851 Free PMC article.
-
Cystatin C as a potential biomarker for dosing of renally excreted drugs.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015 Jul;80(1):20-7. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12602. Epub 2015 May 28. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25655191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacokinetics of Vancomycin among Patients with Chemotherapy-Associated Febrile Neutropenia: Which Would Be the Best Dosing to Obtain Appropriate Exposure?Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Nov 1;11(11):1523. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11111523. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358178 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Vancomycin Levels Using Cystatin C in Overweight and Obese Patients: a Retrospective Cohort Study of Hospitalized Patients.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Dec 16;65(1):e01487-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01487-20. Print 2020 Dec 16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 33106257 Free PMC article.
-
An Update on Population Pharmacokinetic Analyses of Vancomycin, Part I: In Adults.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2020 Jun;59(6):671-698. doi: 10.1007/s40262-020-00866-2. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2020. PMID: 32020531 Review.
References
-
- Appelbaum PC. Microbiology of antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45(Suppl 3):S165–S170. - PubMed
-
- Iwamoto T, Kagawa Y, Kojima M. Clinical efficacy of therapeutic drug monitoring in patients receiving vancomycin. Biol Pharm Bull. 2003;26:876–879. - PubMed
-
- MacGowan AP. Pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and therapeutic drug monitoring of glycopeptides. Ther Drug Monit. 1998;20:473–477. - PubMed
-
- Caregaro L, Menon F, Angeli P, Amodio P, Merkel C, Bortoluzzi A, Alberino F, Gatta A. Limitations of serum creatinine level and creatinine clearance as filtration markers in cirrhosis. Arch Intern Med. 1994;154:201–205. - PubMed
-
- Ross EA, Wilkinson A, Hawkins RA, Danovitch GM. The plasma creatinine concentration is not an accurate reflection of the glomerular filtration rate in stable renal transplant patients receiving cyclosporine. Am J Kidney Dis. 1987;10:113–117. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

