Changes in anti-group a rotavirus antibody seroprevalence and levels in the Western Gyeongnam province of Korea over 16 years
- PMID: 23341712
- PMCID: PMC3546105
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.1.55
Changes in anti-group a rotavirus antibody seroprevalence and levels in the Western Gyeongnam province of Korea over 16 years
Abstract
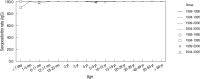
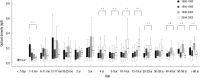
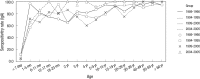
To observe how anti-group A rotavirus antibody seropositivity rates and levels have changed in the western region of Gyeongnam Province, 2,030 serum samples collected at four collection periods (1989-1990, 1994-1995, 1999-2000, and 2004-2005) were tested by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for IgG, and IgA antibodies reacting to recombinant VP6 protein. The seroprevalences exhibit no regular patterns over a 16-yr period. For all four collection periods, the anti-rVP6 IgG levels rose steadily during the first 5 months of life, after which they remained high. However, the 2-9 yr and 10-39 yr groups had significantly higher IgG levels in 1999-2000 and 2004-2005, respectively, than in the other collection periods. The 1-5 mo, 40- ≥ 60 yr, and 4-29 yr groups had significantly higher IgA levels in 1989-1990, 1999-2000, and 2004-2005, respectively. The 4 yr (25.0%), 5-9 yr (18.8%), 10-14 yr (41.1%), 20-29 yr (35.0%), and 30-39 yr (20.0%) groups in 2004-2005 had significant higher IgA seropositivity rate compared to the other three collection periods. These observations suggest that in the western region of Gyeongnam Province since the late 1990s, rotavirus reinfection has occurred more frequently than previously, with all ages being at risk.
Keywords: ELISA; Rotavirus; Seroepidemiology; VP6.
Figures
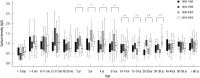
Similar articles
-
Rotavirus vaccination and infection induce VP6-specific IgA responses.J Med Virol. 2017 Feb;89(2):239-245. doi: 10.1002/jmv.24636. Epub 2016 Aug 6. J Med Virol. 2017. PMID: 27431308
-
Seroepidemiology of group C rotavirus infection in England and Wales.Eur J Epidemiol. 2004;19(6):589-95. doi: 10.1023/b:ejep.0000032381.36658.cb. Eur J Epidemiol. 2004. PMID: 15330133
-
Seroepidemiology of human group C rotavirus in South Africa.J Clin Microbiol. 1999 Dec;37(12):4142-4. doi: 10.1128/JCM.37.12.4142-4144.1999. J Clin Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10565947 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-VP6 IgG antibodies against group A and group C rotaviruses in South India.Epidemiol Infect. 2010 Mar;138(3):442-7. doi: 10.1017/S0950268809990732. Epub 2009 Sep 2. Epidemiol Infect. 2010. PMID: 19723364
-
Seroepidemiology of predominant norovirus strains circulating in Korea by using recombinant virus-like particle antigens.Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2013 May;10(5):461-6. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2012.1300. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2013. PMID: 23627928
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Rotavirus. In: Atkinson WHJ, McIntyre L, Wolfe S, editors. Epidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine-preventable Diseases. 10th ed. Washington, DC: Public Health Foundation; 2007. pp. 295–306.
-
- Seo JK, Sim JG. Overview of rotavirus infections in Korea. Pediatr Int. 2000;42:406–410. - PubMed
-
- Chae JH, Kim MJ, Kim DH, Lee KY, Kang JH, Lee JS. Epidemiologic study of rotavirus gastroenteritis, in Daejeon, Korea, 2001-2005. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2007;14:155–161.
-
- Kim JS, Lee HS, Choi JH, Shin YJ, Koo ML, Kim SS, Kim HS, Kim EA, Yoon SW, Kwon JH, et al. A study of acute gastroenteritis in neonates transferred from postpartum care centers. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2003;10:186–192.
-
- Park SI, Kwon HO, Lee JH, Jung SJ. Clinical features of rotaviral gastroenteritis in neonates. Korean J Pediatr. 2005;48:1121–1125.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

