Trends of mortality and cause of death among HIV-infected patients in Korea, 1990-2011
- PMID: 23341714
- PMCID: PMC3546107
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.1.67
Trends of mortality and cause of death among HIV-infected patients in Korea, 1990-2011
Abstract
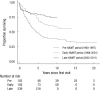
Although a decrease in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)-related mortality has been documented in highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) era, there are no published data comparing specific causes of death between pre-HAART and HAART era in Korea. Mortality and cause of death were analyzed in three treatment periods; pre-HAART (1990-1997), early-HAART (1998-2001), and late-HAART period (2002-2011). The patients were retrospectively classified according to the treatment period in which they were recruited. Although mortality rate per 100 person-year declined from 8.7 in pre-HAART to 4.9 in late-HAART period, the proportion of deaths within 3 months of initial visit to study hospital significantly increased from 15.9% in pre-HAART to 55.1% in late-HAART period (P < 0.001). Overall, 59% of deaths were attributable to AIDS-related conditions, and Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) was the most common cause of death (20.3%). The proportion of PCP as cause of death significantly increased from 8.7% in pre-HAART to 31.8% in late-HAART period (P < 0.001). Despite of significant improvement of survival, there was still a high risk of early death in patients presenting in HAART era, mainly due to late human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) diagnosis and late presentation to care.
Keywords: Antiretroviral Therapy; Cause of Death; HIV; Mortality.
Figures
References
-
- Mocroft A, Ledergerber B, Katlama C, Kirk O, Reiss P, d'Arminio Monforte A, Knysz B, Dietrich M, Phillips AN, Lundgren JD. Decline in the AIDS and death rates in the EUROSIDA study: an observational study. Lancet. 2003;362:22–29. - PubMed
-
- Mocroft A, Vella S, Benfield TL, Chiesi A, Miller V, Gargalianos P, d'Arminio Monforte A, Yust I, Bruun JN, Phillips AN, et al. Changing patterns of mortality across Europe in patients infected with HIV-1. EUROSIDA study group. Lancet. 1998;352:1725–1730. - PubMed
-
- Palella FJ, Jr, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, Loveless MO, Fuhrer J, Satten GA, Aschman DJ, Holmberg SD. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:853–860. - PubMed
-
- Jaggy C, von Overbeck J, Ledergerber B, Schwarz C, Egger M, Rickenbach M, Furrer HJ, Telenti A, Battegay M, Flepp M, et al. Mortality in the Swiss HIV Cohort Study (SHCS) and the Swiss general population. Lancet. 2003;362:877–878. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

