The indoor level of house dust mite allergen is associated with severity of atopic dermatitis in children
- PMID: 23341715
- PMCID: PMC3546108
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.1.74
The indoor level of house dust mite allergen is associated with severity of atopic dermatitis in children
Abstract
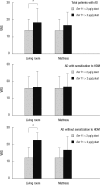
We attempted to investigate the correlation between the severity of atopic dermatitis (AD) in children and the indoor level of house dust mite (HDM) allergens. Ninety-five patients (31.1 ± 19.5 months of age) with AD were enrolled in this study, and serum specific IgE against Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus and D. farinae was measured. The severity of AD was assessed using the visual analogue scale on the same day of house dust collection. Living rooms and mattresses where the child usually slept were vacuumed for 2 minutes and concentrations of Der f 1 were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The skin symptoms were more severe in patients with Der f 1 concentrations in living room > 2 µg/g dust than ≤ 2 µg/g dust (P = 0.018). This difference was noted in AD patients without sensitization to HDM (P = 0.004), but not in patients with sensitization. There was no difference in symptom severity according to Der f 1 concentrations in mattresses (P = 0.062). The severity of skin symptoms is associated with indoor concentrations of HDM in children with AD, and it is likely to act as nonspecific irritants as well as allergens in AD skin lesions.
Keywords: Allergens; Atopic Dermatitis; House Dust Mite.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The correlation between the seasonal variation of house dust mite allergens exposure level in household and the level of asthma control in asthmatic children].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Mar;52(3):177-83. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24824386 Chinese.
-
Immunoglobulin G1 subclass responses can be used to detect specific allergy to the house dust mites Dermatophagoides farinae and Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus in atopic dogs.BMC Vet Res. 2021 Feb 5;17(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12917-021-02768-2. BMC Vet Res. 2021. PMID: 33546688 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of house dust mite avoidance measures in children with atopic dermatitis.Br J Dermatol. 2000 Aug;143(2):379-84. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.2000.03666.x. Br J Dermatol. 2000. PMID: 10951149 Clinical Trial.
-
The detection of house dust mite Dermatophagoides farinae, Der f 2 and Zen-1 allergen-specific immunoglobulin E antibodies in dogs with atopic Dermatitis in Malaysia.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2019 Jun;212:43-49. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2019.05.002. Epub 2019 May 22. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2019. PMID: 31213251
-
Atopic Dermatitis: Identification and Management of Complicating Factors.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 11;21(8):2671. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082671. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32290423 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Environmental determinants of allergy and asthma in early life.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017 Jul;140(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.05.010. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28673399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ceramide AD™ Restores Skin Integrity and Function following Exposure to House Dust Mite.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 25;24(11):9234. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119234. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298186 Free PMC article.
-
Debates in allergy medicine: specific immunotherapy efficiency in children with atopic dermatitis.World Allergy Organ J. 2016 Apr 18;9:15. doi: 10.1186/s40413-016-0106-3. eCollection 2016. World Allergy Organ J. 2016. PMID: 27134696 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in allergen sensitization over the last 30 years in Korea respiratory allergic patients: a single-center.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014 Sep;6(5):434-43. doi: 10.4168/aair.2014.6.5.434. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014. PMID: 25229001 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of indoor house dust mite concentration on canine atopic dermatitis.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Feb 2;10:1078306. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1078306. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 36816188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Voorhorst R, Spieksma-Boezeman MI, Spieksma FT. Is a mite (Dermatophagoides sp.) the producer of the house-dust allergen? Allerg Asthma (Leipz) 1964;10:329–334. - PubMed
-
- Kim KH, Kim KT, Lee SK, Park HS, Lee YM, Nahm DH, Son CH, Yang DK, Roh MS, Choi PJ, et al. Sensitization rates for inhalant allergens in patients with respiratory allergy in Busan. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;25:59–63.
-
- Kuehr J, Frischer T, Meinert R, Barth R, Schraub S, Urbanek R, Karmaus W, Forster J. Sensitization to mite allergens is a risk factor for early and late onset of asthma and for persistence of asthmatic signs in children. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995;95:655–662. - PubMed
-
- Arshad SH, Bateman B, Sadeghnejad A, Gant C, Matthews SM. Prevention of allergic disease during childhood by allergen avoidance: the Isle of Wight prevention study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:307–313. - PubMed
-
- Htut T, Higenbottam TW, Gill GW, Darwin R, Anderson PB, Syed N. Eradication of house dust mite from homes of atopic asthmatic subjects: a double-blind trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;107:55–60. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources