DNA profiling of pineapple cultivars in Japan discriminated by SSR markers
- PMID: 23341750
- PMCID: PMC3528333
- DOI: 10.1270/jsbbs.62.352
DNA profiling of pineapple cultivars in Japan discriminated by SSR markers
Abstract
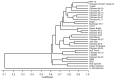
We developed 18 polymorphic simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers in pineapple (Ananas comosus) by using genomic libraries enriched for GA and CA motifs. The markers were used to genotype 31 pineapple accessions, including seven cultivars and 11 breeding lines from Okinawa Prefecture, 12 foreign accessions and one from a related species. These SSR loci were highly polymorphic: the 31 accessions contained three to seven alleles per locus, with an average of 4.1. The values of expected heterozygosity ranged from 0.09 to 0.76, with an average of 0.52. All 31 accessions could be successfully differentiated by the 18 SSR markers, with the exception of 'N67-10' and 'Hawaiian Smooth Cayenne'. A single combination of three markers TsuAC004, TsuAC010 and TsuAC041, was enough to distinguish all accessions with one exception. A phenogram based on the SSR genotypes did not show any distinct groups, but it suggested that pineapples bred in Japan are genetically diversed. We reconfirmed the parentage of 14 pineapple accessions by comparing the SSR alleles at 17 SSR loci in each accession and its reported parents. The obtained information will contribute substantially to protecting plant breeders' rights.
Keywords: Ananas comosus; genetic diversity; parentage; simple sequence repeat.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic Diversity of Pineapple (Ananas comosus) Germplasm in Malaysia Using Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR) Markers.Trop Life Sci Res. 2020 Oct;31(3):15-27. doi: 10.21315/tlsr2020.31.3.2. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Trop Life Sci Res. 2020. PMID: 33214853 Free PMC article.
-
Cultivar identification and genetic relationship of pineapple (Ananas comosus) cultivars using SSR markers.Genet Mol Res. 2015 Nov 25;14(4):15035-43. doi: 10.4238/2015.November.24.11. Genet Mol Res. 2015. PMID: 26634465
-
Genetic Diversity in Various Accessions of Pineapple [Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.] Using ISSR and SSR Markers.Biochem Genet. 2017 Dec;55(5-6):347-366. doi: 10.1007/s10528-017-9803-z. Epub 2017 May 6. Biochem Genet. 2017. PMID: 28478603
-
SSR markers developed using next-generation sequencing technology in pineapple, Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.Breed Sci. 2020 Jun;70(3):415-421. doi: 10.1270/jsbbs.19158. Epub 2020 May 30. Breed Sci. 2020. PMID: 32714066 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling genetic diversity and population structure of pineapple germplasm using genome-wide SNP markers.Mol Genet Genomics. 2025 Jul 19;300(1):71. doi: 10.1007/s00438-025-02275-1. Mol Genet Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40682678 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The genetic relationships of Indian jujube (Ziziphus mauritiana Lam.) cultivars using SSR markers.Heliyon. 2020 Oct 2;6(10):e05078. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05078. eCollection 2020 Oct. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 33072904 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Different Varieties on Quality Characteristics and Microbial Activity of Fresh-Cut Pineapple during Storage.Foods. 2022 Sep 9;11(18):2788. doi: 10.3390/foods11182788. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36140915 Free PMC article.
-
Current status of tropical fruit breeding and genetics for three tropical fruit species cultivated in Japan: pineapple, mango, and papaya.Breed Sci. 2016 Jan;66(1):69-81. doi: 10.1270/jsbbs.66.69. Epub 2016 Jan 1. Breed Sci. 2016. PMID: 27069392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Diversity of Pineapple (Ananas comosus) Germplasm in Malaysia Using Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR) Markers.Trop Life Sci Res. 2020 Oct;31(3):15-27. doi: 10.21315/tlsr2020.31.3.2. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Trop Life Sci Res. 2020. PMID: 33214853 Free PMC article.
-
Leaf margin phenotype-specific restriction-site-associated DNA-derived markers for pineapple (Ananas comosus L.).Breed Sci. 2015 Jun;65(3):276-84. doi: 10.1270/jsbbs.65.276. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Breed Sci. 2015. PMID: 26175625 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Botella, J.R., and Smith, M (2008) Genomics of pineapple, crowning the king of tropical fruits. In: Moore, P. H., and Ming, R. (eds.) Plant Genetics/Genomics: Genomics of Tropical Crop Plants, Springer, USA, pp. 441–451
-
- Bowers, J.E., and Meredith, C.P. (1997) The parentage of a classic wine grape, Cabernet Sauvignon. Nature Genet. 16: 84–87 - PubMed
-
- Bowers, J., Boursiquot, J.M., This, P., Chu, K., Johansson, H., and Meredith, C. (1999) Historical genetics: the parentage of Chardonnay, Gamay and other wine grapes of northeastern France. Science 285: 1562–1565 - PubMed
-
- Brownstein, M.J., Carpten, J.D., and Smith, J.R. (1996) Modulation of nontemplated nucleotide addition by tag DNA polymerase: primer modifications that facilitate genotyping. Biotechniques 20: 1004–1010 - PubMed
-
- Fujii, H., Ogata, T, Shimada, T, Endo, T, Shimizu, T, and Omura, M (2007) Development of a novel algorithm and the computer program for the identification of minimal marker sets of discriminating DNA markers for efficient cultivar identification. Plant & Animal Genomes XV Conference, p. 883 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources