Secondary metabolism and development is mediated by LlmF control of VeA subcellular localization in Aspergillus nidulans
- PMID: 23341778
- PMCID: PMC3547832
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003193
Secondary metabolism and development is mediated by LlmF control of VeA subcellular localization in Aspergillus nidulans
Abstract
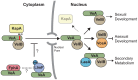
Secondary metabolism and development are linked in Aspergillus through the conserved regulatory velvet complex composed of VeA, VelB, and LaeA. The founding member of the velvet complex, VeA, shuttles between the cytoplasm and nucleus in response to alterations in light. Here we describe a new interaction partner of VeA identified through a reverse genetics screen looking for LaeA-like methyltransferases in Aspergillus nidulans. One of the putative LaeA-like methyltransferases identified, LlmF, is a negative regulator of sterigmatocystin production and sexual development. LlmF interacts directly with VeA and the repressive function of LlmF is mediated by influencing the localization of VeA, as over-expression of llmF decreases the nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio of VeA while deletion of llmF results in an increased nuclear accumulation of VeA. We show that the methyltransferase domain of LlmF is required for function; however, LlmF does not directly methylate VeA in vitro. This study identifies a new interaction partner for VeA and highlights the importance of cellular compartmentalization of VeA for regulation of development and secondary metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
VelB/VeA/LaeA complex coordinates light signal with fungal development and secondary metabolism.Science. 2008 Jun 13;320(5882):1504-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1155888. Science. 2008. PMID: 18556559
-
LaeA control of velvet family regulatory proteins for light-dependent development and fungal cell-type specificity.PLoS Genet. 2010 Dec 2;6(12):e1001226. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001226. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 21152013 Free PMC article.
-
The Aspergillus nidulans velvet domain containing transcription factor VeA is shuttled from cytoplasm into nucleus during vegetative growth and stays there for sexual development, but has to return into cytoplasm for asexual development.PLoS Genet. 2025 Jun 16;21(6):e1011687. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011687. eCollection 2025 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2025. PMID: 40523015 Free PMC article.
-
The VeA regulatory system and its role in morphological and chemical development in fungi.Fungal Genet Biol. 2008 Jul;45(7):1053-61. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2008.03.014. Epub 2008 Mar 31. Fungal Genet Biol. 2008. PMID: 18457967 Review.
-
Coordination of secondary metabolism and development in fungi: the velvet family of regulatory proteins.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2012 Jan;36(1):1-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00285.x. Epub 2011 Jul 13. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2012. PMID: 21658084 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel automethylation reaction in the Aspergillus nidulans LaeA protein generates S-methylmethionine.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 17;288(20):14032-14045. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.465765. Epub 2013 Mar 26. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23532849 Free PMC article.
-
Fungal Morphogenesis, from the Polarized Growth of Hyphae to Complex Reproduction and Infection Structures.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2018 Apr 11;82(2):e00068-17. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00068-17. Print 2018 Jun. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2018. PMID: 29643171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The trans-kingdom identification of negative regulators of pathogen hypervirulence.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2016 Jan;40(1):19-40. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuv042. Epub 2015 Oct 13. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 26468211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering of Global Transcriptional Regulators (GTRs) in Aspergillus for Natural Product Discovery.J Fungi (Basel). 2025 Jun 12;11(6):449. doi: 10.3390/jof11060449. J Fungi (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40558961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of the Relationship between Alternative Respiration and Sterigmatocystin Formation in Aspergillus nidulans.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Apr 20;10(4):168. doi: 10.3390/toxins10040168. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29677138 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bayram O, Krappmann S, Ni M, Bok JW, Helmstaedt K, et al. (2008) VelB/VeA/LaeA complex coordinates light signal with fungal development and secondary metabolism. Science 320: 1504–1506. - PubMed
-
- Sarikaya Bayram O, Bayram O, Valerius O, Park HS, Irniger S, et al. (2010) LaeA control of velvet family regulatory proteins for light-dependent development and fungal cell-type specificity. PLoS Genet 6: e1001226 doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1001226. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bayram O, Braus GH (2012) Coordination of secondary metabolism and development in fungi: the velvet family of regulatory proteins. FEMS Microbiol Rev 36: 1–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

