Increasing trend of colorectal cancer incidence in Korea, 1999-2009
- PMID: 23341785
- PMCID: PMC3546268
- DOI: 10.4143/crt.2012.44.4.219
Increasing trend of colorectal cancer incidence in Korea, 1999-2009
Abstract
Purpose: This study was conducted in order to demonstrate changing trends in colorectal cancer incidence according to sex, age group, and anatomical location in the Korean population.
Materials and methods: Data from the Korea Central Cancer Registry between 1999 and 2009 were analyzed. Annual percent changes (APCs) of sex- and age-specific incidence rates for cancer of the proximal colon (International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th revision [ICD-10] code C18.0-18.5), distal colon (C18.6-18.7), and rectum (C19-20), and male-to-female incidence rate ratios (IRR) were calculated.
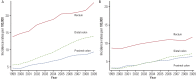
Results: The age-standardized incidence rate (ASR) of colorectal cancer was 27 (per 100,000) in 1999 and increased to 50.2 in 2009 among men (APC, 6.6%). The ASR for women was 17.2 in 1999 and 26.9 in 2009 (APC, 5.1%). The rectum was the most common site of cancer among both men and women during 1999 and 2009. However, the distal colon had the highest APC (10.8% among men and 8.4% among women), followed by the proximal colon (7.9% among men and 6.6% among women), and rectum (5.2% among men and 2.4% among women). The proportion of rectal cancer decreased from 51.5% in 1999 to 47.1% in 2009 among men, and from 50.5% to 42.8% among women. An increase in the male-to-female IRR was observed for distal colon cancer and rectal cancer, whereas the IRR for proximal colon cancer was stable.
Conclusion: The rapid increase in colorectal cancer incidence is mainly attributed to the increase in colon cancer, especially distal colon cancer, and may be explained by a transition of risk factors for subsites or by the effect of colorectal cancer screening.
Keywords: Colorectal neoplasms; Incidence; Korea; Trends.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest relevant to this article was not reported.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. GLOBOCAN 2008 v1.2, Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: IARC Cancer Base No. 10 [Internet] Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2010. [cited 2012 Nov 30]. Available from: http://globocan.iarc.fr.
-
- Gupta AK, Melton LJ, 3rd, Petersen GM, Timmons LJ, Vege SS, Harmsen WS, et al. Changing trends in the incidence, stage, survival, and screen-detection of colorectal cancer: a population-based study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;3:150–158. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous