RNA interference for the treatment of papillomavirus disease
- PMID: 23341856
- PMCID: PMC3547394
- DOI: 10.2174/1874357901206010204
RNA interference for the treatment of papillomavirus disease
Abstract
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)-induced diseases are a significant burden on our healthcare system and current therapies are not curative. Vaccination provides significant prophylactic protection but effective therapeutic treatments will still be required. RNA interference (RNAi) has great promise in providing highly specific therapies for all HPV diseases yet this promise has not been realised. Here we review the research into RNAi therapy for HPV in vitro and in vivo and examine the various targets and outcomes. We discuss the idea of using RNAi with current treatments and address delivery of RNAi, the major issue holding back clinical adoption. Finally, we present our view of a potential path to the clinic.
Keywords: Clinical trial; RNA interference; delivery; human papillomavirus; shRNA.; siRNA.
Figures
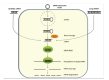
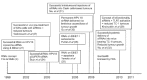
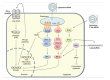
References
-
- Novina CD, Murray MF, Dykxhoorn DM, et al. siRNA-directed inhibition of HIV-1 infection. Nat Med. 2002;8(7):681–6. - PubMed
-
- Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391(6669):806–11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
