Cost-effectiveness analysis of a national neonatal hearing screening program in China: conditions for the scale-up
- PMID: 23341887
- PMCID: PMC3547019
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051990
Cost-effectiveness analysis of a national neonatal hearing screening program in China: conditions for the scale-up
Abstract
Background: In 2009, the Chinese Ministry of Health recommended scale-up of routine neonatal hearing screening - previously performed primarily only in select urban hospitals - throughout the entire country.
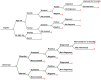
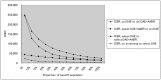
Methods: A decision analytical model for a simulated population of all live births in china was developed to compare the costs and health effects of five mutually exclusive interventions: 1) universal screening using Otoacoustic Emission (OAE) and Automated Auditory Brainstem Response (AABR); 2) universal OAE; 3) targeted OAE and AABR; 4) targeted OAE; and 5) no screening. Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) were calculated for health effects.
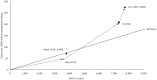
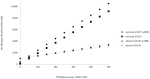
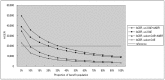
Results and discussion: Based on the cost-effectiveness and potential health outcomes, the optimal path for scale-up would be to start with targeted OAE and then expand to universal OAE and universal OAE plus AABR. Accessibility of screening, diagnosis, and intervention services significantly affect decision of the options.
Conclusion: In conclusion, to achieve cost-effectiveness and best health outcomes of the NHS program, the accessibility of screening, diagnosis, and intervention services should be expanded to reach a larger population. The results are thus expected to be of particular benefit in terms of the 'rolling out' of the national plan.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of neonatal hearing screening program in China: should universal screening be prioritized?BMC Health Serv Res. 2012 Apr 17;12:97. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-12-97. BMC Health Serv Res. 2012. PMID: 22510223 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of portable-automated ABR for universal neonatal hearing screening in India.Front Public Health. 2024 Aug 12;12:1364226. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1364226. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39188791 Free PMC article.
-
Economic evaluation of long-term impacts of universal newborn hearing screening.Int J Audiol. 2017 Jan;56(1):46-52. doi: 10.1080/14992027.2016.1219777. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Int J Audiol. 2017. PMID: 27598544
-
Newborn hearing screening in Hong Kong.Hong Kong Med J. 2006 Jun;12(3):212-8. Hong Kong Med J. 2006. PMID: 16760550 Review.
-
Otoacoustic emission tests in neonatal screening programmes.Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1991;482:73-84. doi: 10.3109/00016489109128029. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1991. PMID: 1897365 Review.
Cited by
-
Economic evaluation of newborn deafness gene screening as a public health intervention in China: a modelling study.BMJ Public Health. 2024 Apr 18;2(1):e000838. doi: 10.1136/bmjph-2023-000838. eCollection 2024 Jun. BMJ Public Health. 2024. PMID: 40018245 Free PMC article.
-
Parental awareness and perspectives on newborn screening in China: a questionnaire-based study.BMC Med Ethics. 2024 Nov 26;25(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s12910-024-01145-6. BMC Med Ethics. 2024. PMID: 39593011 Free PMC article.
-
An Economic Evaluation of Australia's Newborn Hearing Screening Program: A Within-Study Cost-Effectiveness Analysis.Ear Hear. 2022 May/Jun;43(3):972-983. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000001153. Ear Hear. 2022. PMID: 34772837 Free PMC article.
-
Newborn hearing screening program in China: a narrative review of the issues in screening and management.Front Pediatr. 2023 Sep 5;11:1222324. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1222324. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37732008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hearing impairment and its risk factors by newborn screening in north-western India.Matern Health Neonatol Perinatol. 2015 Jul 6;1:17. doi: 10.1186/s40748-015-0018-1. eCollection 2015. Matern Health Neonatol Perinatol. 2015. PMID: 27057334 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lopez AD, Mather C, Ezzati M, Jamison DT, Murray CJL (2006) Global Burden of Disease and Risk Factors. World Bank Publications; Washington DC, USA. - PubMed
-
- Olusanya BO, Newton VE (2007) Global burden of childhood hearing impairment and disease control priorities for developing countries. Lancet 369: 1314–1317. - PubMed
-
- Sininger YS, Doyle KJ, Moore JK (1999) The case for early identification of hearing loss in children. Auditory system development, experimental auditory deprivation, and development of speech perception and hearing. Pediatr Clin North Am 46: 1–14. - PubMed
-
- Moeller MP (2000) Early intervention and language development in children who are deaf and hard of hearing. Pediatrics 106: E43. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy CR, McCann DC, Campbell MJ, Law CM, Mullee M, et al. (2006) Language ability after early detection of permanent childhood hearing impairment. N Eng J Med 354: 2131–2141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

