Image classification of human carcinoma cells using complex wavelet-based covariance descriptors
- PMID: 23341908
- PMCID: PMC3547046
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052807
Image classification of human carcinoma cells using complex wavelet-based covariance descriptors
Abstract
Cancer cell lines are widely used for research purposes in laboratories all over the world. Computer-assisted classification of cancer cells can alleviate the burden of manual labeling and help cancer research. In this paper, we present a novel computerized method for cancer cell line image classification. The aim is to automatically classify 14 different classes of cell lines including 7 classes of breast and 7 classes of liver cancer cells. Microscopic images containing irregular carcinoma cell patterns are represented by subwindows which correspond to foreground pixels. For each subwindow, a covariance descriptor utilizing the dual-tree complex wavelet transform (DT-[Formula: see text]WT) coefficients and several morphological attributes are computed. Directionally selective DT-[Formula: see text]WT feature parameters are preferred primarily because of their ability to characterize edges at multiple orientations which is the characteristic feature of carcinoma cell line images. A Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifier with radial basis function (RBF) kernel is employed for final classification. Over a dataset of 840 images, we achieve an accuracy above 98%, which outperforms the classical covariance-based methods. The proposed system can be used as a reliable decision maker for laboratory studies. Our tool provides an automated, time- and cost-efficient analysis of cancer cell morphology to classify different cancer cell lines using image-processing techniques, which can be used as an alternative to the costly short tandem repeat (STR) analysis. The data set used in this manuscript is available as supplementary material through http://signal.ee.bilkent.edu.tr/cancerCellLineClassificationSampleImages.html.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
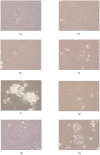

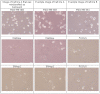
Similar articles
-
Texture Descriptors Ensembles Enable Image-Based Classification of Maturation of Human Stem Cell-Derived Retinal Pigmented Epithelium.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 19;11(2):e0149399. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149399. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26895509 Free PMC article.
-
Computer-aided diagnosis of breast microcalcifications based on dual-tree complex wavelet transform.Biomed Eng Online. 2012 Dec 19;11:96. doi: 10.1186/1475-925X-11-96. Biomed Eng Online. 2012. PMID: 23253202 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Method for Classifying Liver and Brain Tumors Using Convolutional Neural Networks, Discrete Wavelet Transform and Long Short-Term Memory Networks.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Apr 28;19(9):1992. doi: 10.3390/s19091992. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31035406 Free PMC article.
-
Decision support system for age-related macular degeneration using discrete wavelet transform.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2014 Sep;52(9):781-96. doi: 10.1007/s11517-014-1180-8. Epub 2014 Aug 12. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2014. PMID: 25112273
-
Integration of morphological preprocessing and fractal based feature extraction with recursive feature elimination for skin lesion types classification.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2019 Sep;178:201-218. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.06.018. Epub 2019 Jun 16. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2019. PMID: 31416550
Cited by
-
A two-stage classification method for borehole-wall images with support vector machine.PLoS One. 2018 Jun 28;13(6):e0199749. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199749. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29953481 Free PMC article.
-
Mining textural knowledge in biological images: Applications, methods and trends.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2016 Nov 24;15:56-67. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2016.11.002. eCollection 2017. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2016. PMID: 27994798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The development and evaluation of a computerized diagnosis scheme for pneumoconiosis on digital chest radiographs.Biomed Eng Online. 2014 Oct 2;13:141. doi: 10.1186/1475-925X-13-141. Biomed Eng Online. 2014. PMID: 25277489 Free PMC article.
-
Conventional Machine Learning and Deep Learning Approach for Multi-Classification of Breast Cancer Histopathology Images-a Comparative Insight.J Digit Imaging. 2020 Jun;33(3):632-654. doi: 10.1007/s10278-019-00307-y. J Digit Imaging. 2020. PMID: 31900812 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Epigenetic Non-Coding RNA MALAT1/Wnt Signaling Axis as a Therapeutic Approach to Suppress Stemness and Metastasis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cells. 2020 Apr 20;9(4):1020. doi: 10.3390/cells9041020. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32326045 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dundar M, Badve S, Raykar V, Jain R, Sertel O, et al... (2010) A multiple instance learning approach toward optimal classification of pathology slides. In: Pattern Recognition (ICPR), 2010 20th International Conference on. 2732–2735. doi:10.1109/ICPR.2010.669.
-
- Buontempo F, Ersahin T, Missiroli S, Senturk S, Etro D, et al. (2011) Inhibition of akt signaling in hepatoma cells induces apoptotic cell death independent of akt activation status. Investigational New Drugs 29: 1303–1313. - PubMed
-
- Kwitt R, Uhl A, Hafner M, Gangl A, Wrba F, et al... (2010) Predicting the histology of colorectal lesions in a probabilistic framework. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on. 103–110. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW.2010.5543146.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

