Knowledge, attitude and practices of diabetic patients in the United Arab Emirates
- PMID: 23341913
- PMCID: PMC3544806
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052857
Knowledge, attitude and practices of diabetic patients in the United Arab Emirates
Abstract
Introduction: Diabetes self-management education is a cornerstone of diabetes care. However, many diabetics in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) lack sufficient knowledge about their disease due to illiteracy. Thus, before considering any possible intervention it was imperative to assess present knowledge, attitudes, and practices of patients towards the management of diabetes.
Methods: A random sample of 575 DM patients was selected from diabetes outpatient's clinics of Tawam and Al-Ain hospitals in Al-Ain city (UAE) during 2006-2007, and their knowledge attitude and practice assessed using a questionnaire modified from the Michigan Diabetes Research Training Center instrument.
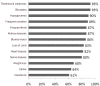
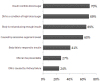
Results: Thirty-one percent of patients had poor knowledge of diabetes. Seventy-two had negative attitudes towards having the disease and 57% had HbA(1c) levels reflecting poor glycemic control. Only seventeen percent reported having adequate blood sugar control, while 10% admitted non-compliance with their medications. Knowledge, practice and attitude scores were all statistically significantly positively, but rather weakly, associated, but none of these scores was significantly correlated with HbA(1c).
Conclusions: The study showed low levels of diabetes awareness but positive attitudes towards the importance of DM care and satisfactory diabetes practices in the UAE. Programs to increase patients' awareness about DM are essential for all diabetics in the UAE in order to improve their understanding, compliance and management and, thereby, their ability to cope with the disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence of diabetes mellitus and its complications in a population-based sample in Al Ain, United Arab Emirates.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007 Dec;78(3):369-77. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2007.04.008. Epub 2007 May 25. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007. PMID: 17532085
-
Knowledge of diabetes among patients in the United Arab Emirates and trends since 2001: a study using the Michigan Diabetes Knowledge Test.East Mediterr Health J. 2017 Jan 23;22(10):742-748. doi: 10.26719/2016.22.10.742. East Mediterr Health J. 2017. PMID: 28134426
-
Epidemiology of Diabetes Mellitus in the United Arab Emirates.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2018;14(6):542-549. doi: 10.2174/1573399813666170920152913. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2018. PMID: 28933305
-
The sunshine under our skin: public knowledge and practices about vitamin D deficiency in Al Ain, United Arab Emirates.Arch Osteoporos. 2019 Nov 22;14(1):111. doi: 10.1007/s11657-019-0671-5. Arch Osteoporos. 2019. PMID: 31758340
-
A Systematic Review on Pharmaceutical Diabetic Care Services in the United Arab Emirates (UAE).Curr Diabetes Rev. 2021;17(6):e122820189559. doi: 10.2174/1573399817999201228210029. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2021. PMID: 33371838
Cited by
-
An examination of the socio-demographic correlates of patient adherence to self-management behaviors and the mediating roles of health attitudes and self-efficacy among patients with coexisting type 2 diabetes and hypertension.BMC Public Health. 2020 Aug 12;20(1):1227. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-09274-4. BMC Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32787809 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge, attitudes and practices towards glycemic control among persons with diabetes mellitus at two tertiary hospitals in Uganda.Afr Health Sci. 2024 Mar;24(1):171-186. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v24i1.22. Afr Health Sci. 2024. PMID: 38962346 Free PMC article.
-
Association of diabetes knowledge with glycemic control and self-care practices among Pakistani people with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019 Aug 14;12:1409-1417. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S209711. eCollection 2019. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019. PMID: 31616171 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary knowledge, attitude and practice among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in Sudan: a hospital-based cross-sectional study.Afr Health Sci. 2021 Mar;21(1):32-40. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v21i1.6. Afr Health Sci. 2021. PMID: 34394278 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes knowledge and glycemic control among type 2 diabetes patients at public hospitals in Debre Berhan, Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 30;20(1):e0317288. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0317288. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39883698 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McPherson ML, Smith SW, Powers A, Zuckerman IH (2008) Association between diabetes patients' knowledge about medications and their blood glucose control. Res Social Adm Pharm Mar; 4 (1) 37–45. - PubMed
-
- Norris SL, Engelgau MM, Narayan KM (2001) Effectiveness of self-management training in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Care 24: 561–87. - PubMed
-
- Ben Abdelaziz A, Thabet H, Soltane I, Gaha K, Gaha R, et al. (2007) Knowledge of patients with type 2 diabetes about their condition in Sousse, Tunisia. East Mediterr Health J May–Jun; 13 (3) 505–14. - PubMed
-
- Kamel NM, Badawy YA, el-Zeiny NA, Merdan IA (1999) Sociodemographic determinants of management behavior of diabetic patients Part 2. Diabetics' knowledge of the disease and their management behavior. EMHJ 5: 5, 974–983. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous