Feeling voices
- PMID: 23341954
- PMCID: PMC3547010
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053585
Feeling voices
Abstract
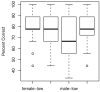
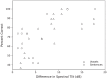
Two experiments investigated deaf individuals' ability to discriminate between same-sex talkers based on vibrotactile stimulation alone. Nineteen participants made same/different judgments on pairs of utterances presented to the lower back through voice coils embedded in a conforming chair. Discrimination of stimuli matched for F0, duration, and perceived magnitude was successful for pairs of spoken sentences in Experiment 1 (median percent correct = 83%) and pairs of vowel utterances in Experiment 2 (median percent correct = 75%). Greater difference in spectral tilt between "different" pairs strongly predicted their discriminability in both experiments. The current findings support the hypothesis that discrimination of complex vibrotactile stimuli involves the cortical integration of spectral information filtered through frequency-tuned skin receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Gault RH (1924) Progress in experiments on tactile interpretation of oral speech. J Abnorm Soc Psychol 19: 155–159.
-
- Reed CM, Rabinowitz WM, Durlach NI, Braida LD, Conway-Fithian S, et al. (1985) Research on the Tadoma method of speech communication. J Acoust Soc Am 77 (1) 247–257. - PubMed
-
- Brooks PL, Frost BJ, Mason JL, Gibson DM (1985) Continuing evaluation of the Queen's University Tactile Vocoder: I Identification of open-set words. J Rehabil Eng 22: 119–128. - PubMed
-
- Brooks PL, Frost BJ, Mason JL, Gibson DM (1985) Continuing evaluation of the Queen's University Tactile Vocoder: II Identification of open set sentences and tracking. J Rehabil Eng 22: 129–138. - PubMed
-
- Brooks PL, Frost BJ, Mason JL, Chung K (1985) Identification of 250 words using a tactile vocoder. J Acoust Soc Am 77: 1576–1579. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

