Monoclonal antibodies against Hepatitis C genotype 3a virus like particle inhibit virus entry in cell culture system
- PMID: 23341957
- PMCID: PMC3546081
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053619
Monoclonal antibodies against Hepatitis C genotype 3a virus like particle inhibit virus entry in cell culture system
Abstract
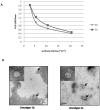
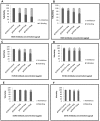
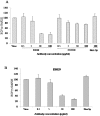
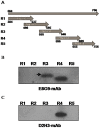
The envelope protein (E1-E2) of Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a major component of the viral structure. The glycosylated envelope protein is considered to be important for initiation of infection by binding to cellular receptor(s) and also known as one of the major antigenic targets to host immune response. The present study was aimed at identifying mouse monoclonal antibodies which inhibit binding of virus like particles of HCV to target cells. The first step in this direction was to generate recombinant HCV-like particles (HCV-LPs) specific for genotypes 3a of HCV (prevalent in India) using the genes encoding core, E1 and E2 envelop proteins in a baculovirus expression system. The purified HCV-LPs were characterized by ELISA and electron microscopy and were used to generate monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) in mice. Two monoclonal antibodies (E8G9 and H1H10) specific for the E2 region of envelope protein of HCV genotype 3a, were found to reduce the virus binding to Huh7 cells. However, the mAbs generated against HCV genotype 1b (D2H3, G2C7, E1B11) were not so effective. More importantly, mAb E8G9 showed significant inhibition of the virus entry in HCV JFH1 cell culture system. Finally, the epitopic regions on E2 protein which bind to the mAbs have also been identified. Results suggest a new therapeutic strategy and provide the proof of concept that mAb against HCV-LP could be effective in preventing virus entry into liver cells to block HCV replication.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combination of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies against Hepatitis C virus E2 protein effectively blocks virus infection.Virus Res. 2016 Sep 15;224:46-57. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.08.010. Epub 2016 Aug 26. Virus Res. 2016. PMID: 27574733
-
A novel neutralizing human monoclonal antibody broadly abrogates hepatitis C virus infection in vitro and in vivo.Antiviral Res. 2017 Dec;148:53-64. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2017.10.015. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Antiviral Res. 2017. PMID: 29074219 Free PMC article.
-
Structural features of envelope proteins on hepatitis C virus-like particles as determined by anti-envelope monoclonal antibodies and CD81 binding.Virology. 2002 Jun 20;298(1):124-32. doi: 10.1006/viro.2002.1463. Virology. 2002. PMID: 12093180
-
Current status and future development of infectious cell-culture models for the major genotypes of hepatitis C virus: Essential tools in testing of antivirals and emerging vaccine strategies.Antiviral Res. 2018 Oct;158:264-287. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.07.014. Epub 2018 Jul 27. Antiviral Res. 2018. PMID: 30059723 Review.
-
Cutting the gordian knot-development and biological relevance of hepatitis C virus cell culture systems.Adv Virus Res. 2008;71:51-133. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)00002-X. Adv Virus Res. 2008. PMID: 18585527 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of a flavonoid isolated from plum (Prunus domestica) as a potent inhibitor of Hepatitis C virus entry.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 21;7(1):3965. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04358-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28638096 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel epitope in the C terminus of hepatitis C virus-E2 protein that induces potent and cross-reactive neutralizing antibodies.J Gen Virol. 2017 May;98(5):962-976. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000735. Epub 2017 May 8. J Gen Virol. 2017. PMID: 28221101 Free PMC article.
References
-
- European Association for the study of Liver (2011) EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: management of hepatitis C virus infection. J Hepatol 55: 245–64. - PubMed
-
- Alter MJ, Margolis HS, Krawczynski K, Judson FN, Mares A, et al. (1992) The natural history of community-acquired hepatitis C in the United States. The Sentinel Counties Chronic non-A, non-B Hepatitis Study Team. N Engl J Med 327: 1899–905. - PubMed
-
- Bartenschlager R, Lohmann V (2000) Replication of hepatitis C virus. J Gen Virol 81: 1631–48. - PubMed
-
- Major ME, Feinstone SM (1997) The molecular virology of hepatitis C. Hepatology. 25: 1527–38. - PubMed
-
- Rice CM (1996) Flaviviridae: the viruses and their replication, p.931–959. In B. N. Fields, D. M. Knipe, and P. M. Howley (ed.), Fields virology, 3rd ed. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, Pa.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

