The pan-genome of the animal pathogen Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis reveals differences in genome plasticity between the biovar ovis and equi strains
- PMID: 23342011
- PMCID: PMC3544762
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053818
The pan-genome of the animal pathogen Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis reveals differences in genome plasticity between the biovar ovis and equi strains
Abstract
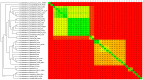
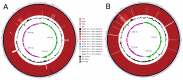
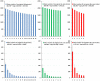
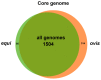
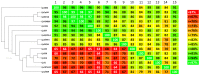
Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis is a facultative intracellular pathogen and the causative agent of several infectious and contagious chronic diseases, including caseous lymphadenitis, ulcerative lymphangitis, mastitis, and edematous skin disease, in a broad spectrum of hosts. In addition, Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis infections pose a rising worldwide economic problem in ruminants. The complete genome sequences of 15 C. pseudotuberculosis strains isolated from different hosts and countries were comparatively analyzed using a pan-genomic strategy. Phylogenomic, pan-genomic, core genomic, and singleton analyses revealed close relationships among pathogenic corynebacteria, the clonal-like behavior of C. pseudotuberculosis and slow increases in the sizes of pan-genomes. According to extrapolations based on the pan-genomes, core genomes and singletons, the C. pseudotuberculosis biovar ovis shows a more clonal-like behavior than the C. pseudotuberculosis biovar equi. Most of the variable genes of the biovar ovis strains were acquired in a block through horizontal gene transfer and are highly conserved, whereas the biovar equi strains contain great variability, both intra- and inter-biovar, in the 16 detected pathogenicity islands (PAIs). With respect to the gene content of the PAIs, the most interesting finding is the high similarity of the pilus genes in the biovar ovis strains compared with the great variability of these genes in the biovar equi strains. Concluding, the polymerization of complete pilus structures in biovar ovis could be responsible for a remarkable ability of these strains to spread throughout host tissues and penetrate cells to live intracellularly, in contrast with the biovar equi, which rarely attacks visceral organs. Intracellularly, the biovar ovis strains are expected to have less contact with other organisms than the biovar equi strains, thereby explaining the significant clonal-like behavior of the biovar ovis strains.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Dorella FA, Pacheco LGC, Oliveira SC, Miyoshi A, Azevedo V (2006) Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis: microbiology, biochemical properties, pathogenesis and molecular studies of virulence. Vet Res 37: 201–218. - PubMed
-
- Lehman KB, Neumann R (1896) Atlas und grundriss der bakeriologie und lehrbuch der speziellen bakteriologischen diagnositk. 1st ed. J.F. Lehmann, Munchen.
-
- Pascual C, Lawson PA, Farrow JA, Gimenez MN, Collins MD (1995) Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Corynebacterium based on 16S rRNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45: 724–728. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

