The interactive effects of cytoskeleton disruption and mitochondria dysfunction lead to reproductive toxicity induced by microcystin-LR
- PMID: 23342045
- PMCID: PMC3547071
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053949
The interactive effects of cytoskeleton disruption and mitochondria dysfunction lead to reproductive toxicity induced by microcystin-LR
Abstract
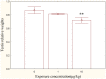
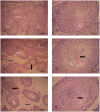
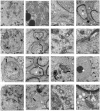
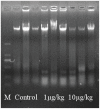
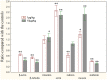
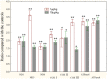
The worldwide occurrence of cyanobacterial blooms evokes profound concerns. The presence of microcystins (MCs) in waters and aquatic food increases the risk to human health. Some recent studies have suggested that the gonad is the second most important target organ of MCs, however, the potential toxicity mechanisms are still unclear. For a better understanding of reproductive toxicity of MCs on animals, we conducted the present experimental investigation. Male rats were intraperitoneally injected with MC-LR for 50 d with the doses of 1 and 10 µg/kg body weight per day. After prolonged exposure to MC-LR, the testes index significantly decreased in 10 µg/kg group. Light microscope observation indicated that the space between the seminiferous tubules was increased. Ultrastructural observation showed some histopathological characteristics, including cytoplasmic shrinkage, cell membrane blebbing, swollen mitochondria and deformed nucleus. Using Q-PCR methods, the transcriptional levels of some cytoskeletal and mitochondrial genes were determined. MC-LR exposure affected the homeostasis of the expression of cytoskeletal genes, causing possible dysfunction of cytoskeleton assembly. In MC-LR treatments, all the 8 mitochondrial genes related with oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) significantly increased. The reactive oxygen species (ROS) level significantly increased in 10 µg/kg group. The mitochondria swelling and DNA damage were also determined in 10 µg/kg group. Hormone levels of testis significantly changed. The present study verified that both cytoskeleton disruption possibly due to cytoskeletal reorganization or depolymerization and mitochondria dysfunction interact with each other through inducing of reactive oxygen species and oxidative phosphorylation, and jointly result in testis impairment after exposure to MC-LR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Involvement of oxidative stress and cytoskeletal disruption in microcystin-induced apoptosis in CIK cells.Aquat Toxicol. 2015 Aug;165:41-50. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.05.009. Epub 2015 May 14. Aquat Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 26022555
-
Co-exposure of microcystin and nitrite enhanced spermatogenic disorders: The role of mtROS-mediated pyroptosis and apoptosis.Environ Int. 2024 Jun;188:108771. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2024.108771. Epub 2024 May 22. Environ Int. 2024. PMID: 38805914
-
Microcystin-LR induced reactive oxygen species mediate cytoskeletal disruption and apoptosis of hepatocytes in Cyprinus carpio L.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 20;8(12):e84768. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084768. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24376844 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of microcystin-LR-induced cytoskeletal disruption in animal cells.Toxicon. 2015 Jul;101:92-100. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2015.05.005. Epub 2015 May 14. Toxicon. 2015. PMID: 25981867 Review.
-
A review of reproductive toxicity of microcystins.J Hazard Mater. 2016 Jan 15;301:381-99. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.08.041. Epub 2015 Aug 30. J Hazard Mater. 2016. PMID: 26521084 Review.
Cited by
-
An overview of the toxic effect of potential human carcinogen Microcystin-LR on testis.Toxicol Rep. 2015 Jan 27;2:289-296. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2015.01.008. eCollection 2015. Toxicol Rep. 2015. PMID: 28962362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microcystin-LR induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in human bronchial epithelial cells.Exp Ther Med. 2016 Aug;12(2):633-640. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3423. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 27446254 Free PMC article.
-
Subchronic Toxicity of Microcystin-LR on Young Frogs (Xenopus laevis) and Their Gut Microbiota.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 12;13:895383. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.895383. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35633706 Free PMC article.
-
Microcystin-LR and its health impacts: Chemistry, transmission routes, mechanisms of toxicity and target organs.Toxicol Rep. 2025 Mar 11;14:101996. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2025.101996. eCollection 2025 Jun. Toxicol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40177604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histopathological Evaluation of the Exposure by Cyanobacteria Cultive Containing [d-Leu¹]Microcystin-LR on Lithobates catesbeianus Tadpoles.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Aug 6;10(8):318. doi: 10.3390/toxins10080318. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30082615 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen J, Xie P, Li L, Xu J (2009) First Identification of the Hepatotoxic Microcystins in the Serum of a Chronically Exposed Human Population Together with Indication of Hepatocellular Damage. Toxicol Sci 108: 81–89. - PubMed
-
- Gupta N, Pant SC, Vijayaraghavan R, Rao PVL (2003) Comparative toxicity evaluation of cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin variants (LR, RR, YR) in mice. Toxicology 188: 285–296. - PubMed
-
- MacKintosh C, Beattie KA, Klumpp S, Cohen P, Codd GA (1990) Cyanobacterial microcystin-LR is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A from both mammals and higher plants. FEBS Lett 264: 187–192. - PubMed
-
- Fu WY, Chen JP, Wang MM, Xu LH (2005) Altered expression of p53, Bcl-2 and Bax induced by microcystin-LR in vivo and in vitro. Toxicon 46: 171–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

