The stigma of migraine
- PMID: 23342079
- PMCID: PMC3546922
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054074
The stigma of migraine
Abstract
Background: People who have a disease often experience stigma, a socially and culturally embedded process through which individuals experience stereotyping, devaluation, and discrimination. Stigma has great impact on quality of life, behavior, and life chances. We do not know whether or not migraine is stigmatizing.
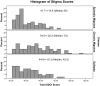
Methods: We studied 123 episodic migraine patients, 123 chronic migraine patients, and 62 epilepsy patients in a clinical setting to investigate the extent to which stigma attaches to migraine, using epilepsy as a comparison. We used the stigma scale for chronic illness, a 24-item questionnaire suitable for studying chronic neurologic diseases, and various disease impact measures.
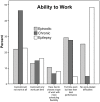
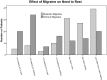
Results: Patients with chronic migraine had higher scores (54.0±20.2) on the stigma scale for chronic illness than either episodic migraine (41.7±14.8) or epilepsy patients (44.6±16.3) (p<0.001). Subjects with migraine reported greater inability to work than epilepsy subjects. Stigma correlated most strongly with the mental component score of the short form of the medical outcomes health survey (SF-12), then with ability to work and migraine disability score for chronic and episodic migraine and the Liverpool impact on epilepsy scale for epilepsy. Analysis of covariance showed adjusted scores for the stigma scale for chronic illness were similar for chronic migraine (49.3; 95% confidence interval, 46.2 to 52.4) and epilepsy (46.5; 95% confidence interval, 41.6 to 51.6), and lower for episodic migraine (43.7; 95% confidence interval, 40.9 to 46.6). Ability to work was the strongest predictor of stigma as measured by the stigma scale for chronic illness.
Conclusion: In our model, adjusted stigma was similar for chronic migraine and epilepsy, which were greater than for episodic migraine. Stigma correlated most strongly with inability to work, and was greater for chronic migraine than epilepsy or episodic migraine because chronic migraine patients had less ability to work.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Goffman E (1963) Stigma: notes on the management of spoiled identity. New York: Simon and Schuster.
-
- Koller M, Kussman J, Lorenz W, Jenkins M, Voss M, et al. (1996) Symptom reporting in cancer patients: the role of negative affect and experienced social stigma. Cancer 77: 983–995. - PubMed
-
- Link BG, Phelan JC (2001) Conceptualizing stigma. Ann Rev Sociol 27: 363–385.
-
- Walton GM, Cohen GL (2011) A brief social-belonging intervention improves academic and health outcomes of minority students. Science 331: 1447–1451. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

