MasABK proteins interact with proteins of the type IV pilin system to affect social motility of Myxococcus xanthus
- PMID: 23342171
- PMCID: PMC3546991
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054557
MasABK proteins interact with proteins of the type IV pilin system to affect social motility of Myxococcus xanthus
Abstract
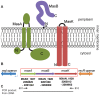
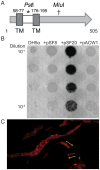
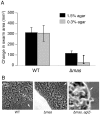
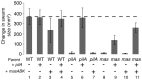
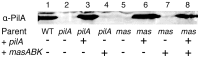
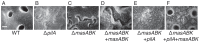
Gliding motility is critical for normal development of spore-filled fruiting bodies in the soil bacterium Myxococcus xanthus. Mutations in mgl block motility and development but one mgl allele can be suppressed by a mutation in masK, the last gene in an operon adjacent to the mgl operon. Deletion of the entire 5.5 kb masABK operon crippled gliding and fruiting body development and decreased sporulation. Expression of pilAGHI, which encodes type IV pili (TFP) components essential for social (S) gliding, several cryptic pil genes, and a LuxR family protein were reduced significantly in the Δmas mutant while expression of the myxalamide operon was increased significantly. Localization and two-hybrid analysis suggest that the three Mas proteins form a membrane complex. MasA-PhoA fusions confirmed that MasA is an integral cytoplasmic membrane protein with a ≈100 amino acid periplasmic domain. Results from yeast two-hybrid assays showed that MasA interacts with the lipoprotein MasB and MasK, a protein kinase and that MasB and MasK interact with one another. Additionally, yeast two-hybrid analysis revealed a physical interaction between two gene products of the mas operon, MasA and MasB, and PilA. Deletion of mas may be accompanied by compensatory mutations since complementation of the Δmas social gliding and developmental defects required addition of both pilA and masABK.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Analysis of type IV pilus and its associated motility in Myxococcus xanthus using an antibody reactive with native pilin and pili.Microbiology (Reading). 2005 Feb;151(Pt 2):353-360. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27614-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2005. PMID: 15699186
-
MglA, a small GTPase, interacts with a tyrosine kinase to control type IV pili-mediated motility and development of Myxococcus xanthus.Mol Microbiol. 2002 Dec;46(5):1399-413. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03258.x. Mol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12453225
-
Direct visualization of the interaction between pilin and exopolysaccharides of Myxococcus xanthus with eGFP-fused PilA protein.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2012 Jan;326(1):23-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2011.02430.x. Epub 2011 Oct 21. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22092602 Free PMC article.
-
Polarity of motility systems in Myxococcus xanthus.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007 Dec;10(6):624-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2007.09.012. Epub 2007 Nov 5. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17981496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gliding motility in bacteria: insights from studies of Myxococcus xanthus.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1999 Sep;63(3):621-41. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.63.3.621-641.1999. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10477310 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development versus predation: Transcriptomic changes during the lifecycle of Myxococcus xanthus.Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 26;13:1004476. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1004476. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36225384 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

