The Staphylococci phages family: an overview
- PMID: 23342361
- PMCID: PMC3528268
- DOI: 10.3390/v4123316
The Staphylococci phages family: an overview
Abstract
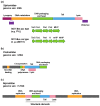
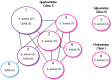
Due to their crucial role in pathogenesis and virulence, phages of Staphylococcus aureus have been extensively studied. Most of them encode and disseminate potent staphylococcal virulence factors. In addition, their movements contribute to the extraordinary versatility and adaptability of this prominent pathogen by improving genome plasticity. In addition to S. aureus, phages from coagulase-negative Staphylococci (CoNS) are gaining increasing interest. Some of these species, such as S. epidermidis, cause nosocomial infections and are therefore problematic for public health. This review provides an overview of the staphylococcal phages family extended to CoNS phages. At the morphological level, all these phages characterized so far belong to the Caudovirales order and are mainly temperate Siphoviridae. At the molecular level, comparative genomics revealed an extensive mosaicism, with genes organized into functional modules that are frequently exchanged between phages. Evolutionary relationships within this family, as well as with other families, have been highlighted. All these aspects are of crucial importance for our understanding of evolution and emergence of pathogens among bacterial species such as Staphylococci.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of novel phages isolated in coagulase-negative staphylococci reveals evolutionary relationships with Staphylococcus aureus phages.J Bacteriol. 2012 Nov;194(21):5829-39. doi: 10.1128/JB.01085-12. Epub 2012 Aug 24. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22923589 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus epidermidis Phages Transduce Antimicrobial Resistance Plasmids and Mobilize Chromosomal Islands.mSphere. 2021 May 12;6(3):e00223-21. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00223-21. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 33980677 Free PMC article.
-
Three proposed new bacteriophage genera of staphylococcal phages: "3alikevirus", "77likevirus" and "Phietalikevirus".Arch Virol. 2014 Feb;159(2):389-98. doi: 10.1007/s00705-013-1833-1. Arch Virol. 2014. PMID: 24022640
-
Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci phages panorama: Genomic diversity and in vitro studies for a therapeutic use.Microbiol Res. 2025 Jan;290:127944. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2024.127944. Epub 2024 Nov 9. Microbiol Res. 2025. PMID: 39550872 Review.
-
Genomics of staphylococcal Twort-like phages--potential therapeutics of the post-antibiotic era.Adv Virus Res. 2012;83:143-216. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394438-2.00005-0. Adv Virus Res. 2012. PMID: 22748811 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic Characterization of Virulence Factors and Related Proteins in Enterococcus Strains from Dairy and Fermented Food Products.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 19;23(18):10971. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810971. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142880 Free PMC article.
-
Toxin-linked mobile genetic elements in major enteric bacterial pathogens.Gut Microbiome (Camb). 2023 Mar 17;4:e5. doi: 10.1017/gmb.2023.2. eCollection 2023. Gut Microbiome (Camb). 2023. PMID: 39295911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy Assessment of Phage Therapy in Treating Staphylococcus aureus-Induced Mastitis in Mice.Viruses. 2022 Mar 16;14(3):620. doi: 10.3390/v14030620. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35337027 Free PMC article.
-
Screening for Highly Transduced Genes in Staphylococcus aureus Revealed Both Lateral and Specialized Transduction.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0242321. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02423-21. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35138167 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Rhinosinusitis, S. aureus Biofilm and Secreted Products, Inflammatory Responses, and Disease Severity.Biomedicines. 2022 Jun 9;10(6):1362. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061362. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740385 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
