Antitumor effect of a polypeptide fraction from Arca subcrenata in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 23342393
- PMCID: PMC3528126
- DOI: 10.3390/md10122782
Antitumor effect of a polypeptide fraction from Arca subcrenata in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
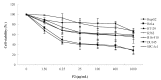
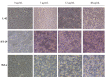
Arca subcrenata Lischke is a marine traditional Chinese medicine. The study investigated the antitumor effects of P2, a polypeptide fraction from A. subcrenata, and its toxicity in vitro and in vivo. The results showed that P2 could inhibit the proliferation of seven tumor cell lines, especially in HeLa and HT-29 cell lines. The IC₅₀ values were 11.43 μg/mL for HeLa and 13.00 μg/mL for HT-29 treated by P2 for 48 h. P2 had little cytotoxicity on normal liver cells (L-02). The maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of P2 on KM mice was 1000 mg/kg by i.p. or i.v. The tumor growth inhibitory ratios of P2 were 26.4%, 41.4% and 46.4% for H-22, and 34.0%, 45.8% and 60.1% for S-180 tumor-bearing mice. The results demonstrated that P2 might be a potential antitumor agent with high efficiency in dose-dependent and time-dependent manners and low toxicity.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A new antiproliferative and antioxidant peptide isolated from Arca subcrenata.Mar Drugs. 2013 May 24;11(6):1800-14. doi: 10.3390/md11061800. Mar Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23708186 Free PMC article.
-
Purification, characterization and in vitro anti-tumor activity of proteins from Arca subcrenata Lischke.Mar Drugs. 2008;6(3):418-30. doi: 10.3390/md20080020. Epub 2008 Jul 10. Mar Drugs. 2008. PMID: 19005577 Free PMC article.
-
Arca subcrenata Polypeptides Inhibit Human Colorectal Cancer HT-29 Cells Growth via Suppression of IGF-1R/Akt/mTOR Signaling and ATP Production.Nutr Cancer. 2020;72(2):260-272. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2019.1625935. Epub 2019 Jul 11. Nutr Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31295033
-
The inhibitory effect of a novel polypeptide fraction from Arca subcrenata on cancer-related inflammation in human cervical cancer HeLa cells.ScientificWorldJournal. 2014 Feb 9;2014:768938. doi: 10.1155/2014/768938. eCollection 2014. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014. PMID: 24683359 Free PMC article.
-
Polypeptide Fraction from Arca subcrenata Induces Apoptosis and G2/M Phase Arrest in HeLa Cells via ROS-Mediated MAPKs Pathways.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:930249. doi: 10.1155/2015/930249. Epub 2015 May 21. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26089952 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Natural Anticancer Peptides from Marine Animal Species: Evidence from In Vitro Cell Model Systems.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 20;16(1):36. doi: 10.3390/cancers16010036. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38201464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review on the Valorization of Bioactives from Marine Animal By-Products for Health-Promoting, Biofunctional Cosmetics.Mar Drugs. 2025 Jul 26;23(8):299. doi: 10.3390/md23080299. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40863616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of marine peptides in cervical and ovarian cancers.Mol Cell Biochem. 2022 Feb;477(2):605-619. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04306-y. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2022. PMID: 34855045 Review.
-
Identification and Characterization of a Novel Protein ASP-3 Purified from Arca subcrenata and Its Antitumor Mechanism.Mar Drugs. 2019 Sep 9;17(9):528. doi: 10.3390/md17090528. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31505835 Free PMC article.
-
A new in vitro anti-tumor polypeptide isolated from Arca inflata.Mar Drugs. 2013 Dec 2;11(12):4773-87. doi: 10.3390/md11124773. Mar Drugs. 2013. PMID: 24317469 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simmons T.L., Andrianasolo E., McPhail K., Flatt P., Gerwick W.H. Marine natural products as anticancer drugs. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005;4:333–342. - PubMed
-
- Wu S.C., Zhang Z.X. Scavenging effects of extracts of Scapharca subcrenata on oxygen free radical. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2010;26:238–240.
-
- Jiao G.L., Yu G.L., Wang W., Zhao X.L., Zhang J.Z., Ewart S.H. Properties of polysaccharides in several seaweeds from Atlantic Canada and their potential anti-influenza viral activities. J. Ocean Univ. China. 2012;11:205–212. doi: 10.1007/s11802-012-1906-x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
