Blood pressure control and treatment adherence in hypertensive patients with metabolic syndrome: protocol of a randomized controlled study based on home blood pressure telemonitoring vs. conventional management and assessment of psychological determinants of adherence (TELEBPMET Study)
- PMID: 23343138
- PMCID: PMC3576326
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-14-22
Blood pressure control and treatment adherence in hypertensive patients with metabolic syndrome: protocol of a randomized controlled study based on home blood pressure telemonitoring vs. conventional management and assessment of psychological determinants of adherence (TELEBPMET Study)
Abstract
Background: Inadequate blood pressure control and poor adherence to treatment remain among the major limitations in the management of hypertensive patients, particularly of those at high risk of cardiovascular events. Preliminary evidence suggests that home blood pressure telemonitoring (HBPT) might help increasing the chance of achieving blood pressure targets and improve patient's therapeutic adherence. However, all these potential advantages of HBPT have not yet been fully investigated.
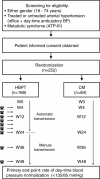
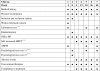
Methods/design: The purpose of this open label, parallel group, randomized, controlled study is to assess whether, in patients with high cardiovascular risk (treated or untreated essential arterial hypertension--both in the office and in ambulatory conditions over 24 h--and metabolic syndrome), long-term (48 weeks) blood pressure control is more effective when based on HBPT and on the feedback to patients by their doctor between visits, or when based exclusively on blood pressure determination during quarterly office visits (conventional management (CM)). A total of 252 patients will be enrolled and randomized to usual care (n = 84) or HBPT (n = 168). The primary study endpoint will be the rate of subjects achieving normal daytime ambulatory blood pressure targets (< 135/85 mmHg) 24 weeks and 48 weeks after randomization. In addition, the study will assess the psychological determinants of adherence and persistence to drug therapy, through specific psychological tests administered during the course of the study. Other secondary study endpoints will be related to the impact of HBPT on additional clinical and economic outcomes (number of additional medical visits, direct costs of patient management, number of antihypertensive drugs prescribed, level of cardiovascular risk, degree of target organ damage and rate of cardiovascular events, regression of the metabolic syndrome).
Discussion: The TELEBPMET Study will show whether HBPT is effective in improving blood pressure control and related medical and economic outcomes in hypertensive patients with metabolic syndrome. It will also provide a comprehensive understanding of the psychological determinants of medication adherence and blood pressure control of these patients.
Trial registration: Clinical Trials.gov: NCT01541566.
Figures

References
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365:217–223. - PubMed
-
- Lawes CM, Vander Hoorn S, Law MR, Elliott P, MacMahon S, Rodgers A. Blood pressure and the global burden of disease, Part II: estimates of attributable burden. J Hypertens. 2000;2006(24):423–430. - PubMed
-
- Malik S, Wong ND, Franklin SS, Kamath TV, L'Italien GJ, Pio JR, Williams GR. Impact of the metabolic syndrome on mortality from coronary heart disease, cardiovascular disease, and all causes in United States adults. Circulation. 2004;110:1245–1250. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000140677.20606.0E. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

