Childhood femoral fracture can lead to premature knee-joint arthritis. 21-year follow-up results: a retrospective study
- PMID: 23343379
- PMCID: PMC3584607
- DOI: 10.3109/17453674.2013.765621
Childhood femoral fracture can lead to premature knee-joint arthritis. 21-year follow-up results: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background and purpose: During the past decades, treatment of pediatric femoral fractures in Finland has changed from mostly non-operative to more operative. In this retrospective study, we analyzed the long-term results of treatment.
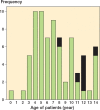
Patients and methods: 74 patients (mean age 7 (0-14) years) with a femoral fracture were treated in Aurora City Hospital in Helsinki during the period 1980-89. 52 of 74 patients participated in this clinical study with a mean follow-up of 21 (16-28) years. Fracture location, treatment mode, time of hospitalization, and fracture alignment at union were assessed. Subjective assessment and range of motion of the hip and knee were evaluated. Leg-length discrepancy and alignment of the lower extremities were measured both clinically and radiographically.
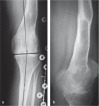
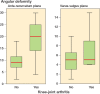
Results: Of the 52 children, 28 had sustained a shaft fracture, 13 a proximal fracture, and 11 a distal fracture. 44 children were treated with traction, 5 by internal fixation, and 3 with cast-immobilization. Length of the hospital treatment averaged 58 (3-156) days and the median traction time was 39 (3-77) days. 21 of the 52 patients had angular malalignment of more than 10 degrees at union. 20 patients experienced back pain. Limping was seen in 10 patients and leg-length discrepancy of more than 15 mm was in 8 of the 52 patients. There was a positive correlation between angular deformity and knee-joint arthritis in radiographs at follow-up in 6 of 15 patients who were over 10 years of age at the time of injury.
Interpretation: Angular malalignment after treatment of femoral fracture may lead to premature knee-joint arthritis. Tibial traction is not an acceptable treatment method for femoral fractures in children over 10 years of age.
Figures
References
-
- Anglen JO, Choi L. Treatment options in pediatric femoral shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19:724–33. - PubMed
-
- Aromaa A, Koskinen S. Health and functional capacity in Finland. Baseline results of the health 2000 health examination survey. http://www.terveys2000.fi/julkaisut/baseline.pdf Publications of the National Public Health Institute, KTL B12/ 2004
-
- Aronson DD, Singer RM, Higgins RF. Skeletal traction for fractures of the femoral shaft in children. A long-term study. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 1987;69:1435–9. - PubMed
-
- Cummings RJ. Paediatric femoral fracture. Comment. Lancet. 2005;365:1116–17. - PubMed
-
- Eckhoff DG, Kramer RC, Alongi CA, VanGeven DP. Femoral anteversion and arthritis of the knee. J Ped Orthop. 1994;14:608–10. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
