A fast least-squares algorithm for population inference
- PMID: 23343408
- PMCID: PMC3602075
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-28
A fast least-squares algorithm for population inference
Abstract
Background: Population inference is an important problem in genetics used to remove population stratification in genome-wide association studies and to detect migration patterns or shared ancestry. An individual's genotype can be modeled as a probabilistic function of ancestral population memberships, Q, and the allele frequencies in those populations, P. The parameters, P and Q, of this binomial likelihood model can be inferred using slow sampling methods such as Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods or faster gradient based approaches such as sequential quadratic programming. This paper proposes a least-squares simplification of the binomial likelihood model motivated by a Euclidean interpretation of the genotype feature space. This results in a faster algorithm that easily incorporates the degree of admixture within the sample of individuals and improves estimates without requiring trial-and-error tuning.
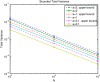
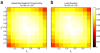
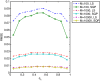
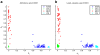
Results: We show that the expected value of the least-squares solution across all possible genotype datasets is equal to the true solution when part of the problem has been solved, and that the variance of the solution approaches zero as its size increases. The Least-squares algorithm performs nearly as well as Admixture for these theoretical scenarios. We compare least-squares, Admixture, and FRAPPE for a variety of problem sizes and difficulties. For particularly hard problems with a large number of populations, small number of samples, or greater degree of admixture, least-squares performs better than the other methods. On simulated mixtures of real population allele frequencies from the HapMap project, Admixture estimates sparsely mixed individuals better than Least-squares. The least-squares approach, however, performs within 1.5% of the Admixture error. On individual genotypes from the HapMap project, Admixture and least-squares perform qualitatively similarly and within 1.2% of each other. Significantly, the least-squares approach nearly always converges 1.5- to 6-times faster.
Conclusions: The computational advantage of the least-squares approach along with its good estimation performance warrants further research, especially for very large datasets. As problem sizes increase, the difference in estimation performance between all algorithms decreases. In addition, when prior information is known, the least-squares approach easily incorporates the expected degree of admixture to improve the estimate.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fast individual ancestry inference from DNA sequence data leveraging allele frequencies for multiple populations.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Jan 16;16:4. doi: 10.1186/s12859-014-0418-7. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25592880 Free PMC article.
-
Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals.Genome Res. 2009 Sep;19(9):1655-64. doi: 10.1101/gr.094052.109. Epub 2009 Jul 31. Genome Res. 2009. PMID: 19648217 Free PMC article.
-
Inferring the ancestry of parents and grandparents from genetic data.PLoS Comput Biol. 2020 Aug 14;16(8):e1008065. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008065. eCollection 2020 Aug. PLoS Comput Biol. 2020. PMID: 32797037 Free PMC article.
-
Analyses of genetic ancestry enable key insights for molecular ecology.Mol Ecol. 2013 Nov;22(21):5278-94. doi: 10.1111/mec.12488. Epub 2013 Sep 19. Mol Ecol. 2013. PMID: 24103088 Review.
-
GADMA2: more efficient and flexible demographic inference from genetic data.Gigascience. 2022 Dec 28;12:giad059. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giad059. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Gigascience. 2022. PMID: 37609916 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fast and efficient estimation of individual ancestry coefficients.Genetics. 2014 Apr;196(4):973-83. doi: 10.1534/genetics.113.160572. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Genetics. 2014. PMID: 24496008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Novembre J, Ramachandran S. Perspectives on human population structure at the cusp of the sequencing era. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2011;12 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

