Combinatorial targeting of FGF and ErbB receptors blocks growth and metastatic spread of breast cancer models
- PMID: 23343422
- PMCID: PMC3672810
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr3379
Combinatorial targeting of FGF and ErbB receptors blocks growth and metastatic spread of breast cancer models
Abstract
Introduction: Targeting receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) with kinase inhibitors is a clinically validated anti-cancer approach. However, blocking one signaling pathway is often not sufficient to cause tumor regression and the effectiveness of individual inhibitors is often short-lived. As alterations in fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) activity have been implicated in breast cancer, we examined in breast cancer models with autocrine FGFR activity the impact of targeting FGFRs in vivo with a selective kinase inhibitor in combination with an inhibitor of PI3K/mTOR or with a pan-ErbB inhibitor.
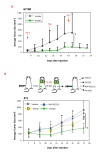
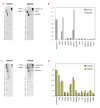
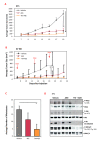
Methods: Using 4T1 or 67NR models of basal-like breast cancer, tumor growth was measured in mice treated with an FGFR inhibitor (dovitinib/TKI258), a PI3K/mTOR inhibitor (NVP-BEZ235) or a pan-ErbB inhibitor (AEE788) individually or in combination. To uncover mechanisms underlying inhibitor action, signaling pathway activity was examined in tumor lysates and transcriptome analysis carried out to identify pathways upregulated by FGFR inhibition. Anti-phosphotyrosine receptor antibody arrays (P-Tyr RTK) were also used to screen 4T1 tumors.
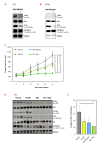
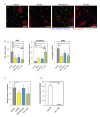
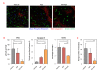
Results: The combination of dovitinib + NVP-BEZ235 causes tumor stasis and strong down-regulation of the FRS2/Erk and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways. P-Tyr RTK arrays identified high levels of P-EGFR and P-ErbB2 in 4T1 tumors. Testing AEE788 in the tumor models revealed that the combination of dovitinib + AEE788 resulted in blockade of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, prolonged tumor stasis and in the 4T1 model, a significant decrease in lung metastasis. The results show that in vivo these breast cancer models become dependent upon co-activation of FGFR and ErbB receptors for PI3K pathway activity.
Conclusions: The work presented here shows that in the breast cancer models examined, the combination of dovitinib + NVP-BEZ235 or dovitinib + AEE788 results in strong inhibition of tumor growth and a block in metastatic spread. Only these combinations strongly down-regulate the FGFR/FRS2/Erk and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways. The resultant decrease in mitosis and increase in apoptosis was consistently stronger in the dovitinib + AEE788 treatment-group, suggesting that targeting ErbB receptors has broader downstream effects compared to targeting only PI3K/mTOR. Considering that sub-classes of human breast tumors co-express ErbB receptors and FGFRs, these results have implications for targeted therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptors blocks PI3K/AKT signaling, induces apoptosis, and impairs mammary tumor outgrowth and metastasis.Cancer Res. 2010 May 15;70(10):4151-62. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4479. Epub 2010 May 11. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20460524
-
Targeting PI3K/mTOR overcomes resistance to HER2-targeted therapy independent of feedback activation of AKT.Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Jul 1;20(13):3507-20. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2769. Epub 2014 May 30. Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24879796
-
Inhibition of Autophagy Increases Proliferation Inhibition and Apoptosis Induced by the PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 in Breast Cancer Cells.Clin Lab. 2015;61(8):1043-51. doi: 10.7754/clin.lab.2015.150144. Clin Lab. 2015. PMID: 26427150
-
Inhibitors of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway: new hope for breast cancer patients.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2010 Jan;5(1):29-57. doi: 10.2174/157489210789702208. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2010. PMID: 19751211 Review.
-
Targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathway in breast cancer.Oncologist. 2011;16(4):404-14. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2010-0402. Epub 2011 Mar 15. Oncologist. 2011. PMID: 21406469 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor neoantigen heterogeneity impacts bystander immune inhibition of pancreatic cancer growth.Transl Oncol. 2020 Dec;13(12):100856. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2020.100856. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Transl Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32862105 Free PMC article.
-
METTL14 Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis Through Regulating EGFR/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway in an m6A-Dependent Manner.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Dec 23;12:13173-13184. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S286275. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 33380825 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the FGFR signaling pathway in cholangiocarcinoma: promise or delusion?Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020 Jul 23;12:1758835920940948. doi: 10.1177/1758835920940948. eCollection 2020. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32754231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synaptopodin-2 plays an important role in the metastasis of breast cancer via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway.Cancer Manag Res. 2018 Jun 18;10:1575-1583. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S162670. eCollection 2018. Cancer Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 30038517 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor splice variants are stable markers of oncogenic transforming growth factor β1 signaling in metastatic breast cancers.Breast Cancer Res. 2014 Mar 11;16(2):R24. doi: 10.1186/bcr3623. Breast Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24618085 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stern HM. Improving treatment of HER2-positive cancers: opportunities and challenges. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:127rv122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

