The disease burden of pertussis in adults 50 years old and older in the United States: a retrospective study
- PMID: 23343438
- PMCID: PMC3610269
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-32
The disease burden of pertussis in adults 50 years old and older in the United States: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: While the incidence of pertussis has increased in adolescents and adults in recent years in the U.S., little is known about the incidence and economic burden of pertussis in older adults. This study provides evidence of the incidence of pertussis and direct medical charges associated with pertussis episodes of care (PEOCs) in adults aged 50 years and older in the U.S.
Methods: PEOCs were divided into periods before and after the initial pertussis diagnosis was made (i.e., the index date) to capture any conditions immediately preceding the pertussis diagnosis that may have represented misdiagnoses and subsequent conditions that may have represented sequelae. Data were extracted from IMS's recently acquired SDI databases of longitudinal, patient-level practitioner claims and hospital operational billing records collected from private practitioners and hospitals, respectively, across the U.S. Patients 50 years and older with one or more ICD-9-CM diagnoses for pertussis/whooping cough and/or a laboratory test positive for Bordetella pertussis between 1/1/2006 and 10/31/2010 were eligible for study inclusion. Resource utilization and charges (i.e., unadjudicated claims) associated with the patient's physician and hospital care were analyzed. The nationally projected incidence of pertussis was estimated using a subsample of patients with the required data necessary for projection.
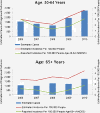
Results: Estimated incidence of diagnosed pertussis ranged from 2.1-4.6 cases per 100,000 people across the two age groups (50-64 and [greater than or equal to] 65) during the years 2006 to 2010. The analysis of charges included 5,748 patients [greater than or equal to] 50 years of age with pertussis. Average charges across the entire episode of care were $1,835 and $14,428 per patient in the outpatient and inpatient settings, respectively. The average number of outpatient (i.e., private practitioner) visits was 2 per patient in both the pre-index and post-index periods.
Conclusions: In the U.S., the incidence of diagnosed pertussis in adults 50 years and older has increased between 2006 and 2010. Healthcare utilization and charges associated with pertussis are substantial, suggesting the need for additional prevention and control strategies and a higher degree of clinical awareness on the part of health care providers. Additional research regarding pertussis in older populations is needed to substantiate these findings.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epidemiology and disease burden of pertussis in the United States among individuals aged 0-64 over a 10-year period (2006-2015).Curr Med Res Opin. 2020 Jan;36(1):127-137. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2019.1662232. Epub 2019 Oct 1. Curr Med Res Opin. 2020. PMID: 31491361
-
The estimated incidence of pertussis in people aged 50 years old in the United States, 2006-2010.BMC Infect Dis. 2015 Nov 19;15:534. doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-1269-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26584525 Free PMC article.
-
The health and economic burden of pertussis in Canada: A microsimulation study.Vaccine. 2019 Nov 20;37(49):7240-7247. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.09.070. Epub 2019 Oct 1. Vaccine. 2019. PMID: 31585727
-
A "new age" in pertussis prevention new opportunities through adult vaccination.Am J Prev Med. 2007 Mar;32(3):177-185. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2006.10.015. Am J Prev Med. 2007. PMID: 17296469 Review.
-
Economic burden of pertussis and the impact of immunization.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005 May;24(5 Suppl):S48-54. doi: 10.1097/01.inf.0000160929.35004.86. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005. PMID: 15876924 Review.
Cited by
-
Epidemiology of Pertussis and Pertussis-Related Complications in Adults: A German Claims Data Analysis.Infect Dis Ther. 2024 Feb;13(2):385-399. doi: 10.1007/s40121-023-00912-z. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Infect Dis Ther. 2024. PMID: 38294623 Free PMC article.
-
Bordetella pertussis in School-Age Children, Adolescents, and Adults: A Systematic Review of Epidemiology, Burden, and Mortality in the Middle East.Infect Dis Ther. 2021 Jun;10(2):719-738. doi: 10.1007/s40121-021-00440-8. Epub 2021 Apr 27. Infect Dis Ther. 2021. PMID: 33905101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Public health management of pertussis in adults: Practical challenges and future strategies.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024 Dec 31;20(1):2377904. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2377904. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024. PMID: 39016172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age related differences in dynamics of specific memory B cell populations after clinical pertussis infection.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 13;9(1):e85227. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085227. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24454823 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of pertussis through adult vaccination.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015;11(7):1744-7. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2015.1038442. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015. PMID: 25912733 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical