Higher magnesium intake is associated with lower fasting glucose and insulin, with no evidence of interaction with select genetic loci, in a meta-analysis of 15 CHARGE Consortium Studies
- PMID: 23343670
- PMCID: PMC3713023
- DOI: 10.3945/jn.112.172049
Higher magnesium intake is associated with lower fasting glucose and insulin, with no evidence of interaction with select genetic loci, in a meta-analysis of 15 CHARGE Consortium Studies
Abstract
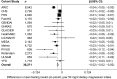
Favorable associations between magnesium intake and glycemic traits, such as fasting glucose and insulin, are observed in observational and clinical studies, but whether genetic variation affects these associations is largely unknown. We hypothesized that single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with either glycemic traits or magnesium metabolism affect the association between magnesium intake and fasting glucose and insulin. Fifteen studies from the CHARGE (Cohorts for Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology) Consortium provided data from up to 52,684 participants of European descent without known diabetes. In fixed-effects meta-analyses, we quantified 1) cross-sectional associations of dietary magnesium intake with fasting glucose (mmol/L) and insulin (ln-pmol/L) and 2) interactions between magnesium intake and SNPs related to fasting glucose (16 SNPs), insulin (2 SNPs), or magnesium (8 SNPs) on fasting glucose and insulin. After adjustment for age, sex, energy intake, BMI, and behavioral risk factors, magnesium (per 50-mg/d increment) was inversely associated with fasting glucose [β = -0.009 mmol/L (95% CI: -0.013, -0.005), P < 0.0001] and insulin [-0.020 ln-pmol/L (95% CI: -0.024, -0.017), P < 0.0001]. No magnesium-related SNP or interaction between any SNP and magnesium reached significance after correction for multiple testing. However, rs2274924 in magnesium transporter-encoding TRPM6 showed a nominal association (uncorrected P = 0.03) with glucose, and rs11558471 in SLC30A8 and rs3740393 near CNNM2 showed a nominal interaction (uncorrected, both P = 0.02) with magnesium on glucose. Consistent with other studies, a higher magnesium intake was associated with lower fasting glucose and insulin. Nominal evidence of TRPM6 influence and magnesium interaction with select loci suggests that further investigation is warranted.
Conflict of interest statement
Author disclosures: The full author list and affiliations are included in Supplemental Table 4 in the “Online Supporting Material” link in the online posting of the article and from the same link in the online table of contents at
Figures

References
-
- Shils ME, Shike M. Modern nutrition in health and disease. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams, & Wilkins; 2006
-
- Fung TT, Manson JE, Solomon CG, Liu S, Willett WC, Hu FB. The association between magnesium intake and fasting insulin concentration in healthy middle-aged women. J Am Coll Nutr. 2003;22:533–8 - PubMed
-
- Humphries S, Kushner H, Falkner B. Low dietary magnesium is associated with insulin resistance in a sample of young, nondiabetic Black Americans. Am J Hypertens. 1999;12:747–56 - PubMed
-
- Ma B, Lawson AB, Liese AD, Bell RA, Mayer-Davis EJ. Dairy, magnesium, and calcium intake in relation to insulin sensitivity: approaches to modeling a dose-dependent association. Am J Epidemiol. 2006;164:449–58 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

