Regulation of renin release via cyclic ADP-ribose-mediated signaling: evidence from mice lacking CD38 gene
- PMID: 23343681
- PMCID: PMC3753399
- DOI: 10.1159/000343348
Regulation of renin release via cyclic ADP-ribose-mediated signaling: evidence from mice lacking CD38 gene
Abstract
Background/aims: Despite extensive studies, the intracellular regulatory mechanism of renin production and release is still poorly understood. The present study was designed to test whether CD38-ADP-ribosylcyclase signaling pathway contributes to the regulation of renin production and release, and to examine whether CD38 gene knockout (CD38(-/-)) can change this important renal endocrinal function.
Methods: ADP-ribosylcyclase activity was estimated utilizing HPLC, cADPR levels from western blot, plasma renin activity from RIA kit, urinary sodium and potassium excretion from fame photometry.
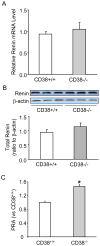
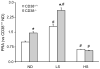
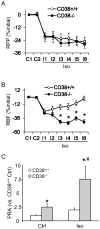
Results: The expression of CD38 and the activity of ADP-ribosylcyclase to produce cyclic ADP-ribose (cADPR) were nearly abolished in the kidney from CD38(-/-) mice, indicating that CD38 gene is a major enzyme responsible for the generation of cADPR in vivo. Mice lacking CD38 gene showed increased plasma renin activity (PRA) in either conscious or anesthetized status (P<0.05). Low salt intake significantly increased, but high salt intake significantly decreased renin release in both CD38(+/+) and CD38(-/-) mice. In acute experiments, it was demonstrated that plasma renin activity (PRA) significantly increased upon isoprenaline infusion in CD38(-/-) mice compared to CD38(+/+) mice. Accompanied with such increase in PRA, glomerular filtration rate (GFR), renal blood flow (RBF), urine volume (UV) and sodium excretion (UNaV) more significantly decreased in CD38(-/-) than CD38(+/+) mice. Similarly, more increases in PRA but more decreases in GFR, RBF, UV and UNaV were observed in CD38(-/-) than CD38(+/+) mice when they had a low renal perfusion pressure (RPP).
Conclusion: CD38-cADPR-mediated signaling may importantly contribute to the maintenance of low PRA and participate in the regulation of renal hemodynamics and excretory function in mice.
Copyright © 2013 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role of cyclic ADP-ribose-Ca2+ signaling in mediating renin production and release in As4.1 cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2007;19(5-6):293-302. doi: 10.1159/000100648. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17495469
-
Synthesis of the Ca2+-mobilizing messengers NAADP and cADPR by intracellular CD38 enzyme in the mouse heart: Role in β-adrenoceptor signaling.J Biol Chem. 2017 Aug 11;292(32):13243-13257. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.789347. Epub 2017 May 24. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28539361 Free PMC article.
-
CD38-cADPR-SERCA Signaling Axis Determines Skeletal Muscle Contractile Force in Response to β-Adrenergic Stimulation.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(5):2017-2030. doi: 10.1159/000489441. Epub 2018 Apr 28. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29723871
-
Resolving the topological enigma in Ca2+ signaling by cyclic ADP-ribose and NAADP.J Biol Chem. 2019 Dec 27;294(52):19831-19843. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV119.009635. Epub 2019 Oct 31. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31672920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD38/cADPR Signaling Pathway in Airway Disease: Regulatory Mechanisms.Mediators Inflamm. 2018 Feb 7;2018:8942042. doi: 10.1155/2018/8942042. eCollection 2018. Mediators Inflamm. 2018. PMID: 29576747 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Intermittent Hypoxia on Metabolism and Cognition.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 26;23(21):12957. doi: 10.3390/ijms232112957. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of NAD (+) , PARP-1, and Sirtuins in Cell Death, Ischemic Brain Injury, and Synchrotron Radiation X-Ray-Induced Tissue Injury.Scientifica (Cairo). 2013;2013:691251. doi: 10.1155/2013/691251. Epub 2013 Dec 10. Scientifica (Cairo). 2013. PMID: 24386592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Meta-Analysis of Blood Pressure Response to β1-Blockers: Results From ICAPS (International Consortium of Antihypertensive Pharmacogenomics Studies).J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Aug 20;8(16):e013115. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.013115. Epub 2019 Aug 19. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31423876 Free PMC article.
-
Possible Molecular Mechanisms of Hypertension Induced by Sleep Apnea Syndrome/Intermittent Hypoxia.Life (Basel). 2024 Jan 22;14(1):157. doi: 10.3390/life14010157. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38276286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Some Aspects of the Renin-Angiotensin-System in Hemodialysis Patients.Kidney Blood Press Res. 2015;40(6):614-22. doi: 10.1159/000368537. Epub 2015 Nov 29. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2015. PMID: 26618349 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee HC, Aarhus R. Wide distribution of an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of cyclic adp-ribose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993;1164:68–74. - PubMed
-
- Lee HC, Aarhus R, Walseth TF. Calcium mobilization by dual receptors during fertilization of sea urchin eggs. Science. 1993;261:352–355. - PubMed
-
- Li PL, Lee HC, Nelson MT, Meininger GA, Van Breemen C. Novel ca2+ signalling mechanisms in vascular myocytes: Symposium overview. Acta Physiol Scand. 2003;179:339–352. - PubMed
-
- Itoh M, Ishihara K, Tomizawa H, Tanaka H, Kobune Y, Ishikawa J, Kaisho T, Hirano T. Molecular cloning of murine bst-1 having homology with cd38 and aplysia adp-ribosyl cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994;203:1309–1317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
