Phospho-ΔNp63α/microRNA feedback regulation in squamous carcinoma cells upon cisplatin exposure
- PMID: 23343772
- PMCID: PMC3594269
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.23598
Phospho-ΔNp63α/microRNA feedback regulation in squamous carcinoma cells upon cisplatin exposure
Abstract
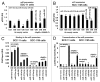
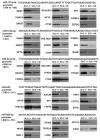
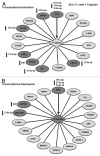
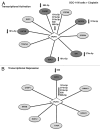
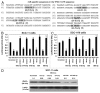
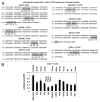
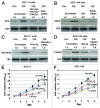
Our previous reports showed that the cisplatin exposure induced the ATM-dependent phosphorylation of ΔNp63a, which is subsequently involved in transcriptional regulation of gene promoters encoding mRNAs and microRNAs in squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) cells upon cisplatin-induced cell death. We showed that phosphorylated (p)-ΔNp63a plays a role in upregulation of pro-apoptotic proteins, while non-p-ΔNp63a is implicated in pro-survival signaling. In contrast to non-p-ΔNp63a, p-ΔNp63a modulated expression of specific microRNAs in SCC cells exposed to cisplatin. These microRNAs were shown to attenuate the expression of several proteins involved in cell death/survival, suggesting the critical role for p-ΔNp63a in regulation of tumor cell resistance to cisplatin. Here, we studied the function of ΔNp63a in transcriptional activation and repression of the specific microRNA promoters whose expression is affected by cisplatin treatment of SCC cells. We quantitatively studied chromatin-associated proteins bound to tumor protein (TP) p63-responsive element, we found that p-ΔNp63a along with certain transcription coactivators (e.g., CARM1, KAT2B, TFAP2A, etc.) necessary to induce gene promoters for microRNAs (630 and 885-3p) or with transcription corepressors (e.g., EZH2, CTBP1, HDACs, etc.) needed to repress promoters for microRNAs (181a-5p, 374a-5p and 519a-3p) in SCC cells exposed to cisplatin.
Keywords: DNA/protein interactions; cisplatin; microRNAs; p53; p63; squamous cell carcinomas.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phospho-ΔNp63α/SREBF1 protein interactions: bridging cell metabolism and cisplatin chemoresistance.Cell Cycle. 2012 Oct 15;11(20):3810-27. doi: 10.4161/cc.22022. Epub 2012 Sep 5. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 22951905 Free PMC article.
-
Phospho-ΔNp63α-dependent regulation of autophagic signaling through transcription and micro-RNA modulation.Cell Cycle. 2012 Mar 15;11(6):1247-59. doi: 10.4161/cc.11.6.19670. Epub 2012 Mar 15. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 22356768 Free PMC article.
-
Phospho-ΔNp63α/microRNA network modulates epigenetic regulatory enzymes in squamous cell carcinomas.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(5):749-61. doi: 10.4161/cc.27676. Epub 2014 Jan 6. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24394434 Free PMC article.
-
Phospho-ΔNp63α/miR-885-3p axis in tumor cell life and cell death upon cisplatin exposure.Cell Cycle. 2011 Nov 15;10(22):3938-47. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.22.18107. Epub 2011 Nov 15. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 22071691 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA regulatory networks and human disease.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Nov;69(21):3529-31. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1123-1. Epub 2012 Aug 25. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22926413 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The microRNA feedback regulation of p63 in cancer progression.Oncotarget. 2015 Apr 20;6(11):8434-53. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3020. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25726529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Negative feedback between TAp63 and Mir-133b mediates colorectal cancer suppression.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 27;7(52):87147-87160. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13515. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27894087 Free PMC article.
-
How MicroRNAs Command the Battle against Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 28;25(11):5865. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115865. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alleviation of Toxicity Caused by Overactivation of Pparα through Pparα-Inducible miR-181a2.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017 Dec 15;9:195-206. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2017.09.008. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017. PMID: 29246298 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Protein p63/microRNA Network in Epithelial Cancer Cells.Curr Genomics. 2013 Nov;14(7):441-52. doi: 10.2174/13892029113146660011. Curr Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24396276 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
