Sensorimotor adaptation changes the neural coding of somatosensory stimuli
- PMID: 23343897
- PMCID: PMC3628028
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00719.2012
Sensorimotor adaptation changes the neural coding of somatosensory stimuli
Abstract
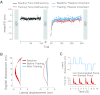
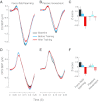
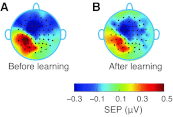
Motor learning is reflected in changes to the brain's functional organization as a result of experience. We show here that these changes are not limited to motor areas of the brain and indeed that motor learning also changes sensory systems. We test for plasticity in sensory systems using somatosensory evoked potentials (SEPs). A robotic device is used to elicit somatosensory inputs by displacing the arm in the direction of applied force during learning. We observe that following learning there are short latency changes to the response in somatosensory areas of the brain that are reliably correlated with the magnitude of motor learning: subjects who learn more show greater changes in SEP magnitude. The effects we observe are tied to motor learning. When the limb is displaced passively, such that subjects experience similar movements but without experiencing learning, no changes in the evoked response are observed. Sensorimotor adaptation thus alters the neural coding of somatosensory stimuli.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Somatosensory evoked potentials show plastic changes following a novel motor training task with the thumb.Clin Neurophysiol. 2015 Mar;126(3):575-80. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2014.05.020. Epub 2014 Jun 5. Clin Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 24957977 Clinical Trial.
-
Functional Plasticity in Somatosensory Cortex Supports Motor Learning by Observing.Curr Biol. 2016 Apr 4;26(7):921-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016.01.064. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Curr Biol. 2016. PMID: 26972317 Free PMC article.
-
Subclinical Neck Pain Leads to Differential Changes in Early Somatosensory Evoked Potentials in Response to a Novel Force Matching Tracking Task.J Integr Neurosci. 2024 Jan 15;23(1):10. doi: 10.31083/j.jin2301010. J Integr Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38287858
-
Evoked potentials as indices of adaptation in the somatosensory system in humans: a review and prospectus.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1993 May-Aug;18(2):151-206. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(93)90001-g. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1993. PMID: 8339106 Review.
-
Integrated technology for evaluation of brain function and neural plasticity.Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2004 Feb;15(1):263-306. doi: 10.1016/s1047-9651(03)00124-4. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2004. PMID: 15029909 Review.
Cited by
-
Somatosensory cortical excitability changes precede those in motor cortex during human motor learning.J Neurophysiol. 2019 Oct 1;122(4):1397-1405. doi: 10.1152/jn.00383.2019. Epub 2019 Aug 7. J Neurophysiol. 2019. PMID: 31390294 Free PMC article.
-
Robot-assisted training of the kinesthetic sense: enhancing proprioception after stroke.Front Hum Neurosci. 2015 Jan 5;8:1037. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.01037. eCollection 2014. Front Hum Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25601833 Free PMC article.
-
Lombard Effect in Individuals With Nonphonotraumatic Vocal Hyperfunction: Impact on Acoustic, Aerodynamic, and Vocal Fold Vibratory Parameters.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2022 Aug 17;65(8):2881-2895. doi: 10.1044/2022_JSLHR-21-00508. Epub 2022 Aug 5. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2022. PMID: 35930680 Free PMC article.
-
A robot-aided visuomotor wrist training induces gains in proprioceptive and movement accuracy in the contralateral wrist.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 5;11(1):5281. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84767-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33674684 Free PMC article.
-
Passive Proprioceptive Training Alters the Sensitivity of Muscle Spindles to Imposed Movements.eNeuro. 2022 Jan 28;9(1):ENEURO.0249-21.2021. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0249-21.2021. Print 2022 Jan-Feb. eNeuro. 2022. PMID: 35022185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alary F, Doyon B, Loubinoux I, Carel C, Boulanouar K, Ranjeva JP, Celsis P, Chollet F. Event-related potentials elicited by passive movements in humans: characterization, source analysis, and comparison to fMRI. Neuroimage 8: 377–390, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Alary F, Simões C, Jousmäki V, Forss N, Hari R. Cortical activation associated with passive movements of the human index finger: an MEG study. Neuroimage 15: 691–696, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Bernier PM, Burle B, Vidal F, Hasbroucq T, Blouin J. Direct evidence for cortical suppression of somatosensory afferents during visuomotor adaptation. Cereb Cortex 19: 2106–2113, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Bötzel K, Ecker C, Schulze S. Topography and dipole analysis of reafferent electrical brain activity following the Bereitschaftspotential. Exp Brain Res 114: 352–361, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Burdet E, Osu R, Franklin DW, Milner TE, Kawato M. The central nervous system stabilizes unstable dynamics by learning optimal impedance. Nature 414: 446–449, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

