The role of the VEGF-C/VEGFRs axis in tumor progression and therapy
- PMID: 23344023
- PMCID: PMC3565253
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms14010088
The role of the VEGF-C/VEGFRs axis in tumor progression and therapy
Abstract
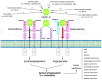
Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) has been identified as a multifaceted factor participating in the regulation of tumor angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. VEGF-C is not only expressed in endothelial cells, but also in tumor cells. VEGF-C signaling is important for progression of various cancer types through both VEGF receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) and VEGF receptor-3 (VEGFR-3). Likewise, both receptors are expressed mainly on endothelial cells, but also expressed in tumor cells. The dimeric VEGF-C undergoes a series of proteolytic cleavage steps that increase the protein binding affinity to VEGFR-3; however, only complete processing, removing both the N- and C-terminal propeptides, yields mature VEGF-C that can bind to VEGFR-2. The processed VEGF-C can bind and activate VEGFR-3 homodimers and VEGFR-2/VEGFR-3 heterodimers to elicit biological responses. High levels of VEGF-C expression and VEGF-C/VEGFRs signaling correlate significantly with poorer prognosis in a variety of malignancies. Therefore, the development of new drugs that selectively target the VEGF-C/VEGFRs axis seems to be an effective means to potentiate anti-tumor therapies in the future.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential Receptor Binding and Regulatory Mechanisms for the Lymphangiogenic Growth Factors Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)-C and -D.J Biol Chem. 2016 Dec 30;291(53):27265-27278. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.736801. Epub 2016 Nov 16. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27852824 Free PMC article.
-
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor cediranib blocks ligand-induced vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 activity and lymphangiogenesis.Cancer Res. 2008 Jun 15;68(12):4754-62. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5809. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18559522
-
The role of the VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 axis in cancer progression.Br J Cancer. 2007 Feb 26;96(4):541-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603487. Epub 2006 Dec 12. Br J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17164762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), VEGF receptors and their inhibitors for antiangiogenic tumor therapy.Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34(12):1785-8. doi: 10.1248/bpb.34.1785. Biol Pharm Bull. 2011. PMID: 22130231 Review.
-
Differential effects of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor PTK787/ZK222584 on tumor angiogenesis and tumor lymphangiogenesis.Mol Cancer Ther. 2009 Jan;8(1):55-63. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0679. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009. PMID: 19139113
Cited by
-
Compartment model predicts VEGF secretion and investigates the effects of VEGF trap in tumor-bearing mice.Front Oncol. 2013 Jul 30;3:196. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2013.00196. eCollection 2013. Front Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23908970 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of BMP signaling suppresses metastasis in mammary cancer.Oncogene. 2015 May 7;34(19):2437-49. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.189. Epub 2014 Jul 7. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 24998846 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of siRNA targeting BMPR-II on the biological activities of human liver cancer cells and its mechanism.Cancer Cell Int. 2014 Jun 19;14:55. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-14-55. eCollection 2014. Cancer Cell Int. 2014. PMID: 25002834 Free PMC article.
-
Cholenic acid derivative UniPR1331 impairs tumor angiogenesis via blockade of VEGF/VEGFR2 in addition to Eph/ephrin.Cancer Gene Ther. 2022 Jul;29(7):908-917. doi: 10.1038/s41417-021-00379-5. Epub 2021 Aug 23. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022. PMID: 34426652 Free PMC article.
-
VEGF-C and Mortality in Patients With Suspected or Known Coronary Artery Disease.J Am Heart Assoc. 2018 Nov 6;7(21):e010355. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.010355. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018. PMID: 30554564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Senger D.R., Galli S.J., Dvorak A.M., Perruzzi C.A., Harvey V.S., Dvorak H.F. Tumor cells secrete a vascular permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid. Science. 1983;219:983–985. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N., Henzel W.J. Pituitary follicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989;161:851–858. - PubMed
-
- Veikkola T., Karkkainen M., Claesson-Welsh L., Alitalo K. Regulation of angiogenesis via vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Cancer Res. 2000;60:203–212. - PubMed
-
- Lohela M., Bry M., Tammela T., Alitalo K. Vegfs and receptors involved in angiogenesis versus lymphangiogenesis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009;21:154–165. - PubMed
-
- Roy H., Bhardwaj S., Yla-Herttuala S. Biology of vascular endothelial growth factors. FEBS Lett. 2006;580:2879–2887. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

