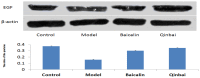
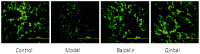
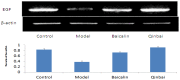
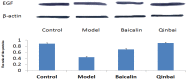
Modulation of P1 and EGF expression by Baicalin
- PMID: 23344025
- PMCID: PMC3565255
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms14010146
Modulation of P1 and EGF expression by Baicalin
Abstract
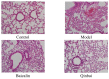
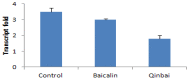
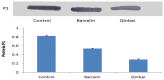
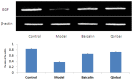
Mycoplasma pneumoniae (M. pneumoniae) is increasingly recognized as a major cause of acute respiratory tract infections. Today, macrolides are used in the primary treatment of M. pneumoniae infection. However, with the increasing prevalence of strains resistant to macrolides, as well as reports of toxicity and adverse side effects, it is necessary to develop an alternative therapeutic agent. A compound recipe - Qinbaiqingfei pellets (Qinbai) - have already been approved in China as the first effective traditional Chinese medicine to be used against M. pneumoniae. Herein, we characterize the mechanism by which Qinbai interacts with M. pneumoniae and lung epithelial cells. The fact that Baicalin is the key component of Qingbai leads us to believe its study is important to elucidating the mechanism of the action of Qinbai. In this study, we describe the complex impact of Baicalin on the adhesin protein P1 of M. pneumoniae and on the expression of epidermal growth factor (EGF) in BALB/c mice and A549 cells infected with M. pneumonia. We draw the conclusion that Baicalin not only cured M. pneumoniae infection by inhibiting P1 expression, but also enhanced the repair of lung epithelial cells by upregulating EGF. Finally, we demonstrate that Baicalin plays a role in Qinbai treatment.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The inhibition of Platycodin D on Mycoplasma pneumoniae proliferation and its effect on promoting cell growth after anti-Mycoplasma pneumoniae treatment.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 Jan 13;4:192. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00192. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25629010 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of Platycodin D on the expression of cytoadherence proteins P1 and P30 in Mycoplasma pneumoniae models.Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2017 Jan;49:188-193. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2017.01.001. Epub 2017 Jan 3. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28073091
-
Protective immunity induced by a novel P1 adhesin C-terminal anchored mRNA vaccine against Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in BALB/c mice.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Mar 4;13(3):e0214024. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02140-24. Epub 2025 Jan 20. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 39831768 Free PMC article.
-
Adhesion proteins of Mycoplasma pneumoniae.Front Biosci. 2007 Jan 1;12:690-9. doi: 10.2741/2093. Front Biosci. 2007. PMID: 17127329 Review.
-
Overview of antimicrobial options for Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia: focus on macrolide resistance.Clin Respir J. 2017 Jul;11(4):419-429. doi: 10.1111/crj.12379. Epub 2015 Oct 13. Clin Respir J. 2017. PMID: 26365811 Review.
Cited by
-
Baicalin relieves Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection‑induced lung injury through regulating microRNA‑221 to inhibit the TLR4/NF‑κB signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Aug;24(2):571. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12210. Epub 2021 Jun 10. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34109422 Free PMC article.
-
Histomorphological and Immunohistochemical Study of Dacomitinib-Induced Ileal Mucositis in Rats with the Possible Protection by Baicalin.J Microsc Ultrastruct. 2022 Nov 9;11(3):135-144. doi: 10.4103/jmau.jmau_115_20. eCollection 2023 Jul-Sep. J Microsc Ultrastruct. 2022. PMID: 38025187 Free PMC article.
-
Baicalin ameliorates oxidative stress and apoptosis by restoring mitochondrial dynamics in the spleen of chickens via the opposite modulation of NF-κB and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway during Mycoplasma gallisepticum infection.Poult Sci. 2019 Dec 1;98(12):6296-6310. doi: 10.3382/ps/pez406. Poult Sci. 2019. PMID: 31376349 Free PMC article.
-
A Study Based on Metabolomics, Network Pharmacology, and Experimental Verification to Explore the Mechanism of Qinbaiqingfei Concentrated Pills in the treatment of Mycoplasma Pneumonia.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 4;12:761883. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.761883. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34803705 Free PMC article.
-
The inhibition of Platycodin D on Mycoplasma pneumoniae proliferation and its effect on promoting cell growth after anti-Mycoplasma pneumoniae treatment.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 Jan 13;4:192. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00192. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25629010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu C.L., Wang G.Q., Zhang B., Xu H., Hu L.P., He X.F. Mycoplasma. pneumoniae pneumonia in hospitalized children diagnosed at acute stage by paired sera. Chin. Med. J. 2010;123:3444–3450. - PubMed
-
- Bébéar C., Pereyre S., Peuchant O. Mycoplasma pneumoniae: Susceptibility and resistance to antibiotics. Future Microbiol. 2011;6:423–431. - PubMed
-
- Morozumi M., Takahashi T., Ubukata K. Macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae: Characteristics of isolates and clinical aspects of community-acquired pneumonia. J. Infect. Chemother. 2010;16:78–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

