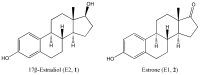
Quantitative structure-activity relationships predicting the antioxidant potency of 17β-estradiol-related polycyclic phenols to inhibit lipid peroxidation
- PMID: 23344051
- PMCID: PMC3565329
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms14011443
Quantitative structure-activity relationships predicting the antioxidant potency of 17β-estradiol-related polycyclic phenols to inhibit lipid peroxidation
Abstract
The antioxidant potency of 17β-estradiol and related polycyclic phenols has been well established. This property is an important component of the complex events by which these types of agents are capable to protect neurons against the detrimental consequences of oxidative stress. In order to relate their molecular structure and properties with their capacity to inhibit lipid peroxidation, a marker of oxidative stress, quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) studies were conducted. The inhibition of Fe3+-induced lipid peroxidation in rat brain homogenate, measured through an assay detecting thiobarbituric acid reactive substances for about seventy compounds were correlated with various molecular descriptors. We found that lipophilicity (modeled by the logarithm of the n-octanol/water partition coefficient, logP) was the property that influenced most profoundly the potency of these compounds to inhibit lipid peroxidation in the biological medium studied. Additionally, the important contribution of the bond dissociation enthalpy of the phenolic O-H group, a shape index, the solvent-accessible surface area and the energy required to remove an electron from the highest occupied molecular orbital were also confirmed. Several QSAR equations were validated as potentially useful exploratory tools for identifying or designing novel phenolic antioxidants incorporating the structural backbone of 17β-estradiol to assist therapy development against oxidative stress-associated neurodegeneration.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Establishment of a quantitative structure-activity relationship model for evaluating and predicting the protective potentials of phenolic antioxidants on lipid peroxidation.J Pharm Sci. 2003 Mar;92(3):475-84. doi: 10.1002/jps.10301. J Pharm Sci. 2003. PMID: 12587109
-
17Beta-estradiol protects against quinolinic acid-induced lipid peroxidation in the rat brain.Metab Brain Dis. 2000 Dec;15(4):267-74. doi: 10.1023/a:1011119107765. Metab Brain Dis. 2000. PMID: 11383551
-
QSAR study of antioxidant activity of wine polyphenols.Eur J Med Chem. 2009 Jan;44(1):400-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2008.03.001. Epub 2008 Mar 10. Eur J Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 18403057
-
Role of Sulphur and Heavier Chalcogens on the Antioxidant Power and Bioactivity of Natural Phenolic Compounds.Biomolecules. 2022 Jan 6;12(1):90. doi: 10.3390/biom12010090. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35053239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oestrogens as antioxidant cardioprotectants.Biochem Soc Trans. 1997 Feb;25(1):54-9. doi: 10.1042/bst0250054. Biochem Soc Trans. 1997. PMID: 9056843 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
A Novel Prodrug Approach for Central Nervous System-Selective Estrogen Therapy.Molecules. 2019 Nov 19;24(22):4197. doi: 10.3390/molecules24224197. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31752337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
10β,17α-Dihydroxyestra-1,4-dien-3-one: A Bioprecursor Prodrug Preferentially Producing 17α-Estradiol in the Brain for Targeted Neurotherapy.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018 Nov 21;9(11):2528-2533. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00184. Epub 2018 Jun 5. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29843514 Free PMC article.
-
Retina-Targeted Delivery of 17β-Estradiol by the Topically Applied DHED Prodrug.Pharmaceutics. 2020 May 16;12(5):456. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12050456. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32429388 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Feminizing Estrogens Do Not Exhibit Antidepressant-like Activity.J Pharm Drug Res. 2016;1(1):1-6. Epub 2016 May 15. J Pharm Drug Res. 2016. PMID: 28239683 Free PMC article.
-
Computational studies of free radical-scavenging properties of phenolic compounds.Curr Top Med Chem. 2015;15(2):85-104. doi: 10.2174/1568026615666141209143702. Curr Top Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25547098 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mariani E., Polidori M.C., Cherubini A., Mecocci P. Oxidative stress in brain aging, neurodegenerative and vascular diseases: An overview. J. Chromatogr. B. 2005;827:65–75. - PubMed
-
- Niki E. Lipid peroxidation products as oxidative stress biomarkers. Biofactors. 2008;34:171–180. - PubMed
-
- Wagner B.A., Buettner G.R., Burns C.P. Free radical-mediated lipid peroxidation in cells: Oxidizability is a function of cell lipid bis-allylic hydrogen content. Biochemistry. 1995;33:4449–4453. - PubMed
-
- Mancuso C., Barone E., Guido P., Miceli F., Di Domenico F., Perluigi M., Santangelo R., Preziosi P. Inhibition of lipid peroxidation and protein oxidation by endogenous and exogenous antioxidants in rat brain microsomes in vitro. Neurosci. Lett. 2012;19:101–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical