Diversity of peptides produced by Nodularia spumigena from various geographical regions
- PMID: 23344154
- PMCID: PMC3564153
- DOI: 10.3390/md11010001
Diversity of peptides produced by Nodularia spumigena from various geographical regions
Abstract
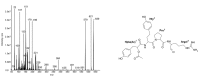
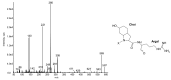
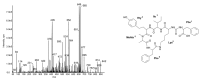
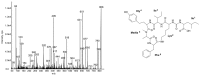
Cyanobacteria produce a great variety of non-ribosomal peptides. Among these compounds, both acute toxins and potential drug candidates have been reported. The profile of the peptides, as a stable and specific feature of an individual strain, can be used to discriminate cyanobacteria at sub-population levels. In our work, liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry was used to elucidate the structures of non-ribosomal peptides produced by Nodularia spumigena from the Baltic Sea, the coastal waters of southern Australia and Lake Iznik in Turkey. In addition to known structures, 9 new congeners of spumigins, 4 aeruginosins and 12 anabaenopeptins (nodulapeptins) were identified. The production of aeruginosins by N. spumigena was revealed in this work for the first time. The isolates from the Baltic Sea appeared to be the richest source of the peptides; they also showed a higher diversity in peptide profiles. The Australian strains were characterized by similar peptide patterns, but distinct from those represented by the Baltic and Lake Iznik isolates. The results obtained with the application of the peptidomic approach were consistent with the published data on the genetic diversity of the Baltic and Australian populations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chemical and Genetic Diversity of Nodularia spumigena from the Baltic Sea.Mar Drugs. 2016 Nov 10;14(11):209. doi: 10.3390/md14110209. Mar Drugs. 2016. PMID: 27834904 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudoaeruginosins, nonribosomal peptides in Nodularia spumigena.ACS Chem Biol. 2015 Mar 20;10(3):725-33. doi: 10.1021/cb5004306. Epub 2014 Dec 5. ACS Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25419633
-
New structural variants of aeruginosin produced by the toxic bloom forming cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 6;8(9):e73618. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073618. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24040002 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial diversity and function in the Baltic Sea with an emphasis on cyanobacteria.Ambio. 2007 Apr;36(2-3):180-5. doi: 10.1579/0044-7447(2007)36[180:bdafit]2.0.co;2. Ambio. 2007. PMID: 17520932 Review.
-
Genetic diversity within populations of cyanobacteria assessed by analysis of single filaments.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2002 Aug;81(1-4):197-202. doi: 10.1023/a:1020510516829. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2002. PMID: 12448718 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Cyanobacterial Bloom Extracts on the Biomass, Chl-a, MC and Other Oligopeptides Contents in a Natural Planktothrix agardhii Population.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Apr 22;17(8):2881. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17082881. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32331227 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Characterization of New Peptide Variants Produced by Cyanobacteria from the Brazilian Atlantic Coastal Forest Using Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Tandem Mass Spectrometry.Mar Drugs. 2015 Jun 18;13(6):3892-919. doi: 10.3390/md13063892. Mar Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26096276 Free PMC article.
-
Production of High Amounts of Hepatotoxin Nodularin and New Protease Inhibitors Pseudospumigins by the Brazilian Benthic Nostoc sp. CENA543.Front Microbiol. 2017 Oct 9;8:1963. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01963. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29062311 Free PMC article.
-
Fragmentation mass spectra dataset of linear cyanopeptides - microginins.Data Brief. 2020 Jun 10;31:105825. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2020.105825. eCollection 2020 Aug. Data Brief. 2020. PMID: 32671141 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Evaluation of Spumigin Analogues Library with Thrombin Inhibitory Activity.Mar Drugs. 2018 Oct 27;16(11):413. doi: 10.3390/md16110413. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30373260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ishida K., Christiansen G., Yoshida W.Y., Kurmayer R., Welker M., Valls N., Bonjoch J., Hertweck C., Börner T., Hemscheidt T., et al. Biosynthesis and structure of aeruginoside 126A and 126B, cyanobacterial peptide glycosides bearing a 2-carboxy-6-hydroxyoctahydroindole moiety. Chem. Biol. 2007;14:565–576. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2007.04.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fewer D.P., Jokela J., Rouhiainen L., Wahlsten M., Koskenniemi K., Stal L.J., Sivonen K. The non-ribosomal assembly and frequent occurrence of the protease inhibitors spumigins in the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena. Mol. Microbiol. 2009;73:924–937. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06816.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

