Beneficial effects of marine algal compounds in cosmeceuticals
- PMID: 23344156
- PMCID: PMC3564164
- DOI: 10.3390/md11010146
Beneficial effects of marine algal compounds in cosmeceuticals
Abstract
The name "cosmeceuticals" is derived from "cosmetics and pharmaceuticals", indicating that a specific product contains active ingredients. Marine algae have gained much importance in cosmeceutical product development due to their rich bioactive compounds. In the present review, marine algal compounds (phlorotannins, sulfated polysaccharides and tyrosinase inhibitors) have been discussed toward cosmeceutical application. In addition, atopic dermatitis and the possible role of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) in skin-related diseases have been explored extensively for cosmeceutical products. The proper development of marine algae compounds will be helpful in cosmeceutical product development and in the development of the cosmeceutical industry.
Figures
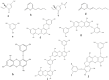


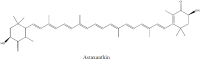
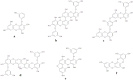



References
-
- Holdt S.L., Kraan S. Bioactive compounds in seaweed: Functional food applications and legislation. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011;23:543–597. doi: 10.1007/s10811-010-9632-5. - DOI
-
- Borowitzka M.A. Microalgae as sources of pharmaceuticals and other biologically active compounds. J. Appl. Phycol. 1995;7:3–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00003544. - DOI
-
- Metting B., Pyne J.W. Biologically active compounds from microalgae. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1986;8:386–394. doi: 10.1016/0141-0229(86)90144-4. - DOI
-
- Moore R.E. Volatile compounds from marine algae. Acc. Chem. Res. 1977;10:40–47. doi: 10.1021/ar50110a002. - DOI
-
- Cannell R.J.P. Algae as a source of biologically active products. Pestic. Sci. 2006;39:147–153. doi: 10.1002/ps.2780390208. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

