Structural characterization of de novo designed L5K5W model peptide isomers with potent antimicrobial and varied hemolytic activities
- PMID: 23344198
- PMCID: PMC6270530
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules18010859
Structural characterization of de novo designed L5K5W model peptide isomers with potent antimicrobial and varied hemolytic activities
Abstract
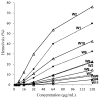
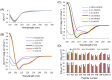
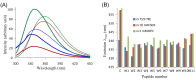
In an effort to develop short antimicrobial peptides with simple amino acid compositions, we generated a series of undecapeptide isomers having the L(5)K(5)W formula. Amino acid sequences were designed to be perfectly amphipathic when folded into a helical conformation by converging leucines onto one side and lysines onto the other side of the helical axis. The single tryptophans, whose positions were varied in the primary structures, were located commonly at the critical amphipathic interface in the helical wheel projection. Helical conformations and the tryptophanyl environments of the 11 L(5)K(5)W peptides were confirmed and characterized by circular dichroism, fluorescence and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. All of the isomers exhibited a potent, broad-spectrum of antibacterial activity with just a slight variance in individual potency, whereas their hemolytic activities against human erythrocytes were significantly diversified. Interestingly, helical dispositions and fluorescence blue shifts of the peptides in aqueous trifluoroethanol solutions, rather than in detergent micelles, showed a marked linear correlation with their hemolytic potency. These results demonstrate that our de novo design strategy for amphipathic helical model peptides is effective for developing novel antimicrobial peptides and their hemolytic activities can be estimated in correlation with structural parameters.
Figures

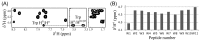
Similar articles
-
Latarcins: versatile spider venom peptides.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Dec;72(23):4501-22. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2016-x. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26286896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
De novo generation of antimicrobial LK peptides with a single tryptophan at the critical amphipathic interface.J Pept Sci. 2009 Sep;15(9):583-8. doi: 10.1002/psc.1149. J Pept Sci. 2009. PMID: 19544481
-
Effects and mechanisms of the secondary structure on the antimicrobial activity and specificity of antimicrobial peptides.J Pept Sci. 2015 Jul;21(7):561-8. doi: 10.1002/psc.2767. Epub 2015 Mar 30. J Pept Sci. 2015. PMID: 25826179
-
The π Configuration of the WWW Motif of a Short Trp-Rich Peptide Is Critical for Targeting Bacterial Membranes, Disrupting Preformed Biofilms, and Killing Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Biochemistry. 2017 Aug 8;56(31):4039-4043. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00456. Epub 2017 Jul 26. Biochemistry. 2017. PMID: 28731688 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of chemical modifications on the antimicrobial and hemolytic activity of helical amphipathic peptide Lasioglossin LL-III.Amino Acids. 2023 Nov;55(11):1531-1544. doi: 10.1007/s00726-023-03326-w. Epub 2023 Sep 22. Amino Acids. 2023. PMID: 37737904 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel gramicidin formulations in cationic lipid as broad-spectrum microbicidal agents.Int J Nanomedicine. 2014 Jun 30;9:3183-92. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S65289. eCollection 2014. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014. PMID: 25061295 Free PMC article.
-
Latarcins: versatile spider venom peptides.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Dec;72(23):4501-22. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2016-x. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26286896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Road from Host-Defense Peptides to a New Generation of Antimicrobial Drugs.Molecules. 2018 Feb 1;23(2):311. doi: 10.3390/molecules23020311. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29389911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
10-mer and 9-mer WALK Peptides with Both Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Activities.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Nov 10;11(11):1588. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11111588. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358242 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiofilm assay for antimicrobial peptides combating the sulfate-reducing bacteria Desulfovibrio vulgaris.Microbiologyopen. 2023 Aug;12(4):e1376. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.1376. Microbiologyopen. 2023. PMID: 37642483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fjell C.D., Hiss J.A., Hancock R.E.W., Schneider G. Designing antimicrobial peptides: Form follows function. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012;11:37–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

